Gum-based nanocomposites for the removal of metals and dyes from waste water
- PMID: 37674071
- PMCID: PMC10567940
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-023-29389-6
Gum-based nanocomposites for the removal of metals and dyes from waste water
Abstract
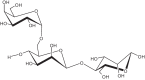
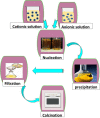
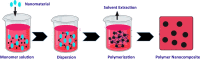
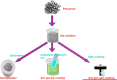
The importance of water for all living organisms is unquestionable and protecting its sources is crucial. In order to reduce water contaminants, like toxic metals and organic dyes, researchers are exploring different techniques, such as adsorption, photocatalytic degradation, and electrolysis. Novel materials are also being sought. In particular, biopolymers like guar gum and xanthan gum, that are eco-friendly, non-toxic, reusable, abundant and cost-effective, have enormous potential. Gum-based nanocomposites can be prepared and used for removing heavy metals and colored dyes by adsorption and degradation, respectively. This review explains the significance of gum-based nanomaterials in waste water treatment, including preparative steps, characterization techniques, kinetics models, and the degradation and adsorption mechanisms involved.
Keywords: Adsorption; Degradation; Guar gum; Gum-based nanomaterials; Waste water treatment; Xanthan gum.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Adegoke KA, Oluwatobi A, Ogunmodede J, Araoye A, Bello O. Metal-organic frameworks as adsorbents for sequestering organic pollutants from wastewater. Mater Chem Phys. 2020;253:123246. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123246. - DOI
-
- Adimule V, Kerur S, Chinnam S, Yallur BC, Nandi SS (2022) Guar gum and its nanocomposites as prospective materials for miscellaneous applications: A short review. Top Catal:1–14
-
- Ahmad, A. I., S. Hassan, T. Ahmed, Z. Imran, S. S. Batool and A. Abbass (2022). “The impact of tungsten oxide (WO3) nanoparticles, embedded in Guar gum based hydrogel for water treatment applications.”
-
- Ahmad R, Haseeb S. Absorptive removal of Pb2+, Cu2+ and Ni2+ from the aqueous solution by using groundnut husk modified with Guar Gum (GG): kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Groundw Sustain Dev. 2015;1(1-2):41–49. doi: 10.1016/j.gsd.2015.11.001. - DOI
-
- Ahmad R, Mirza A. Synthesis of Guar gum/bentonite a novel bionanocomposite: isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic studies for the removal of Pb (II) and crystal violet dye. J Mol Liq. 2018;249:805–814. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2017.11.082. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

