Epigenetic regulation of autophagy-related genes: Implications for neurodevelopmental disorders
- PMID: 37674294
- PMCID: PMC10761153
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2250217
Epigenetic regulation of autophagy-related genes: Implications for neurodevelopmental disorders
Abstract
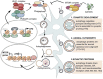
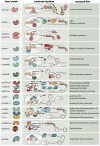
Macroautophagy/autophagy is an evolutionarily highly conserved catabolic process that is important for the clearance of cytosolic contents to maintain cellular homeostasis and survival. Recent findings point toward a critical role for autophagy in brain function, not only by preserving neuronal health, but especially by controlling different aspects of neuronal development and functioning. In line with this, mutations in autophagy-related genes are linked to various key characteristics and symptoms of neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs), including autism, micro-/macrocephaly, and epilepsy. However, the group of NDDs caused by mutations in autophagy-related genes is relatively small. A significant proportion of NDDs are associated with mutations in genes encoding epigenetic regulatory proteins that modulate gene expression, so-called chromatinopathies. Intriguingly, several of the NDD-linked chromatinopathy genes have been shown to regulate autophagy-related genes, albeit in non-neuronal contexts. From these studies it becomes evident that tight transcriptional regulation of autophagy-related genes is crucial to control autophagic activity. This opens the exciting possibility that aberrant autophagic regulation might underly nervous system impairments in NDDs with disturbed epigenetic regulation. We here summarize NDD-related chromatinopathy genes that are known to regulate transcriptional regulation of autophagy-related genes. Thereby, we want to highlight autophagy as a candidate key hub mechanism in NDD-related chromatinopathies.Abbreviations: ADNP: activity dependent neuroprotector homeobox; ASD: autism spectrum disorder; ATG: AutTophaGy related; CpG: cytosine-guanine dinucleotide; DNMT: DNA methyltransferase; EHMT: euchromatic histone lysine methyltransferase; EP300: E1A binding protein p300; EZH2: enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit; H3K4me3: histone 3 lysine 4 trimethylation; H3K9me1/2/3: histone 3 lysine 9 mono-, di-, or trimethylation; H3K27me2/3: histone 3 lysine 27 di-, or trimethylation; hiPSCs: human induced pluripotent stem cells; HSP: hereditary spastic paraplegia; ID: intellectual disability; KANSL1: KAT8 regulatory NSL complex subunit 1; KAT8: lysine acetyltransferase 8; KDM1A/LSD1: lysine demethylase 1A; MAP1LC3B: microtubule associated protein 1 light chain 3 beta; MTOR: mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase; MTORC1: mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1; NDD: neurodevelopmental disorder; PHF8: PHD finger protein 8; PHF8-XLID: PHF8-X linked intellectual disability syndrome; PTM: post-translational modification; SESN2: sestrin 2; YY1: YY1 transcription factor; YY1AP1: YY1 associated protein 1.
Keywords: Autophagy related gene expression; chromatinopathies; epigenetics; neurodevelopmental disorders; neuronal autophagy.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous