Basic Human Needs in the Elderly Receiving Palliative Care: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 37674669
- PMCID: PMC10179993
- DOI: 10.14475/jhpc.2022.25.4.178
Basic Human Needs in the Elderly Receiving Palliative Care: A Scoping Review
Abstract
Purpose: This scoping review identified scientific evidence on basic human needs (BHNs) in the elderly receiving palliative care.
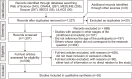
Methods: Systematic searches were conducted using six electronic databases (PubMed, CINAHL, Scopus, Lilacs, IBECS, and Web of Science). The initial search resulted in 1,227 articles, of which 104 were identified as potentially relevant. Fifty-three articles that met the inclusion criteria were identified and included in the final analysis.
Results: Using the three hierarchical dimensions of the BHN model, 17 needs were organised, with five in the psychobiological dimension, 10 in the psychosocial dimension, and two in the psychospiritual dimension. These needs reflect the importance of care with dignity and relief from suffering for the elderly in palliative care.
Conclusion: Recognising impaired BHNs in elderly people receiving palliative care will contribute to better care plans for the elderly, considering the multiple bio-psycho-social-spiritual dimensions of BHNs. This review points to a predominance of psychosocial needs.
Keywords: Aged; Hospice and palliative care nursing; Needs assessment; Palliative care; Review; Terminal care.
Copyright © 2022 by Korean Society for Hospice and Palliative Care.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported. AUTHOR’S CONTRIBUTIONS Conception or design of the work: TAM, RSS. Data collection: TAM, AOD. Data analysis and interpretation: TAM, AOD, RSS. Drafting the article: TAM, MBA, RSS. Critical revision of the article: TAM, MBA, EBM, ARS, RSS. Final approval of the version to be published: all authors.
Figures
References
-
- Steinhauser KE, Alexander S, Olsen MK, Stechuchak KM, Zervakis J, Ammarell N, et al. Addressing patient emotional and existential needs during serious illness: results of the outlook randomized controlled trial. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2017;54:898–908. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2017.06.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maslow AH. A theory of human motivation. Psychological Review. 1943;50:370–96. doi: 10.1037/h0054346. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous