The effect of Jendrassik maneuver on the persistence of the peroneal nerve F-wave
- PMID: 37674799
- PMCID: PMC10478551
- DOI: 10.5606/tftrd.2023.10931
The effect of Jendrassik maneuver on the persistence of the peroneal nerve F-wave
Abstract
Objectives: This study investigated whether peroneal nerve F-wave persistence increased when the Jendrassik maneuver (JM) was performed, aiming to obtain information about the physiology of F-waves and JM.
Patients and methods: Thirty healthy individuals (HIs; 17 females, 13 males; mean age: 33.6±8.2 years; range, 23-50 years) were included in the prospective experimental study conducted between June 15, 2021, and December 15, 2021. Nerve conduction studies of peroneal, superficial peroneal, posterior tibial, and sural nerves were performed in one extremity of each HI. The peroneal nerve F-wave study was performed at rest (Study 1), during JM (Study 2), and after JM (Study 3). F-wave persistence of the peroneal nerve, maximum F-wave amplitude (ampF-wavemax), mean F-wave amplitude (ampF-wavemean), minimum F-wave latency, and the ratio of ampF-wavemean to maximum M amplitude (F/M ratio) were analyzed.
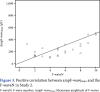
Results: The mean peroneal nerve F-wave persistence in Study 1, Study 2, and Study 3 was 28.7±23.9%, 52.3±32.1%, and 34.7±29.0%, respectively. F-wave persistence in Study 2 was higher compared to Studies 1 and 3 (p<0.001 and p<0.001, respectively). Moreover, ampF-wavemax, ampF-wavemean, and F/M ratio in Study 2 were higher than Studies 1 and 3 (p=0.026 and p=0.021 for ampF-wavemean; p=0.015 and p=0.003 for ampF-wavemax; p=0.033 and p=0.015 for F/M ratio, respectively). F-wave persistence in Study 2 was positively correlated with ampF-wavemax and ampF-wavemean (p<0.001, r= 0.717; p<0.001, r=0.786, respectively).
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that JM increased F-wave persistence and amplitude. Jendrassik maneuver may show its effect through motor neuron excitability.
Keywords: F-wave; F-wave persistence; Jendrassik maneuver; motor neuron excitability; peroneal nerve..
Copyright © 2023, Turkish Society of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declared no conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Sample size for the estimation of F-wave parameters in healthy volunteers and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017 Mar 7;97(9):670-674. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2017.09.007. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28297826 Chinese.
-
Study of F-wave Components in a Control Population of Young Adults.Cureus. 2025 Mar 23;17(3):e81059. doi: 10.7759/cureus.81059. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40271325 Free PMC article.
-
F-wave latency, the most sensitive nerve conduction parameter in patients with diabetes mellitus.Muscle Nerve. 1997 Oct;20(10):1296-302. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4598(199710)20:10<1296::aid-mus12>3.0.co;2-1. Muscle Nerve. 1997. PMID: 9324086
-
Dynamic F wave study in patients suffering from peripheral arterial occlusive disease.Acta Neurol Scand. 2007 Feb;115(2):84-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.2006.00725.x. Acta Neurol Scand. 2007. PMID: 17212610
-
The use of F-wave and sural potential in the diagnosis of subclincal diabetic neuropathy in Saudi patients.Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2001 Jul;6(3):169-74. Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2001. PMID: 24185364
References
-
- Rajabally YA, Durand MC, Mitchell J, Orlikowski D, Nicolas G. Electrophysiological diagnosis of Guillain-Barré syndrome subtype: Could a single study suffice. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015;86:115–119. - PubMed
-
- Jerath N, Kimura J. F wave, A wave, H reflex, and blink reflex. Handb Clin Neurol. 2019;160:225–239. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
