Early detection system of risk factors for diabetes mellitus type 2 utilization of machine learning-random forest
- PMID: 37675209
- PMCID: PMC10479022
- DOI: 10.4103/jfcm.jfcm_33_23
Early detection system of risk factors for diabetes mellitus type 2 utilization of machine learning-random forest
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of morbidity and mortality for type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) is still increasing because of changing lifestyles. There needs to be a means of controlling the rise in the incidence of the disease. Many researchers have utilized technological advances such as machine learning for disease prevention and control, especially in noncommunicable conditions. Researchers are, therefore, interested in creating an early detection system for risk factors of type 2 diabetes.
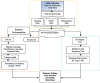
Materials and methods: The study was conducted in February 2022, utilizing secondary surveillance data from Puskesmas Johar Baru, Jakarta, in 2019, 2020, and 2021. Data was analyzed utilizing various bivariate and multivariate statistical methods at 5% significance level and machine learning methods (random forest algorithm) with an accuracy rate of >80%. The data for the three years was cleaned, normalized, and merged.
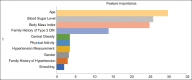
Results: The final population was 65,533 visits out of the initial data of 196,949, and the final number of DM 2 population was 2766 out of the initial data of 9903. Age, gender, family history of DM, family history of hypertension, hypertension, high blood sugar levels, obesity, and central obesity were significantly associated with type 2 DM. Family history was the strongest risk factor of all independent variables, odds ratio of 15.101. The classification results of feature importance, with an accuracy rate of 84%, obtained in order were age, blood sugar level, and body mass index.
Conclusion: Blood sugar level is the most influential factor in the incidence of DM in Puskesmas Johar Baru. In other words, a person with a family history of type 2 diabetes, at unproductive age, of female gender, and of excessive weight can avoid type 2 diabetes if they can regularly maintain their blood sugar levels.
Keywords: Detection; determinants; diabetes mellitus type 2; risk factors.
Copyright: © 2023 Journal of Family and Community Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diabetes mellitus and hypertension based on the family history and 2-h postprandial blood sugar in the Ann-Lo district (northern Taiwan).Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1993 Apr;20(1):75-85. doi: 10.1016/0168-8227(93)90026-2. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1993. PMID: 8344134
-
A survey on diabetes risk prediction using machine learning approaches.J Family Med Prim Care. 2022 Nov;11(11):6929-6934. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_502_22. Epub 2022 Dec 16. J Family Med Prim Care. 2022. PMID: 36993028 Free PMC article.
-
[Polish Multicenter Study on Diabetes Epidemiology (PMSDE)--1998-2000].Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2001 Sep;106(3):751-8. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2001. PMID: 11928582 Polish.
-
Prevalence and risk factors of type-2 diabetes mellitus in Ethiopia: systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 5;11(1):21733. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01256-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34741064 Free PMC article.
-
Data-driven modeling and prediction of blood glucose dynamics: Machine learning applications in type 1 diabetes.Artif Intell Med. 2019 Jul;98:109-134. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2019.07.007. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Artif Intell Med. 2019. PMID: 31383477 Review.
Cited by
-
Machine learning and artificial intelligence in type 2 diabetes prediction: a comprehensive 33-year bibliometric and literature analysis.Front Digit Health. 2025 Mar 27;7:1557467. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2025.1557467. eCollection 2025. Front Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40212895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, update. 5th edn. 2012. [Last accessed on 2023 Jan 04]. Available from: http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas/5e/Update2023 . - PubMed
-
- Nabhani N, Widiyastuti Y. The effect of honey on the healing process of gangrene wounds in patients with diabetes mellitus. Media Publikasi Penelitian. 2017;15:69.
-
- Kemenkes RI. Infodatin 2020 Diabetes Mellitus Data and Information Center Indonesian Ministry of Health. 2020
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources