Validation of liquid biopsy for ESR1-mutation analysis in hormone-sensitive breast cancer: a pooled meta-analysis
- PMID: 37675216
- PMCID: PMC10477975
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1221773
Validation of liquid biopsy for ESR1-mutation analysis in hormone-sensitive breast cancer: a pooled meta-analysis
Abstract
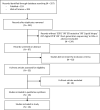
Several retrospective and prospective studies have shown that genomic alterations in Estrogen-receptor one (ESR1) can be characterized not only in tissue samples but also by sequencing circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in liquid biopsy. Therefore, liquid biopsy is a potential noninvasive surrogate for tissue biopsy. This meta-analysis was designed to compare the prevalence of ESR 1 mutation detected with liquid biopsy and tissue biopsy. A pooled meta-analysis of studies published between 1 January 2007 and 1 March 2021 was conducted regarding the methodologies used for ESR1 mutation analysis. Liquid biopsy is a valid, inexpensive, and attractive noninvasive alternative to tumor biopsies for the identification of ESR1 mutations. Liquid biopsy for ESR 1 analysis would facilitate regular testing, allowing monitoring of the sensitivity to ET and guiding treatment strategies.
Keywords: ESR1; digital PCR; liquid biopsy; metastasized breast cancer; next-generation sequencing.
Copyright © 2023 Najim, Papadimitriou, Broeckx, Huizing and Tjalma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
ESR1 mutations in HR+/HER2-metastatic breast cancer: Enhancing the accuracy of ctDNA testing.Cancer Treat Rev. 2023 Dec;121:102642. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2023.102642. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Cancer Treat Rev. 2023. PMID: 37864956 Review.
-
Hybrid capture-based genomic profiling of circulating tumor DNA from patients with estrogen receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer.Ann Oncol. 2017 Nov 1;28(11):2866-2873. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx490. Ann Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28945887 Free PMC article.
-
ESR1 Gene Mutation in Hormone Receptor-Positive HER2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients: Concordance Between Tumor Tissue and Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 11;11:625636. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.625636. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33777770 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of ESR1 Mutations in Tissue and Liquid Biopsy with Novel Next-Generation Sequencing and Digital Droplet PCR Assays: Insights from Multi-Center Real Life Data of Almost 6000 Patients.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Apr 9;17(8):1266. doi: 10.3390/cancers17081266. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40282442 Free PMC article.
-
Standardized molecular pathology workflow for ctDNA-based ESR1 testing in HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2024 Sep;201:104427. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2024.104427. Epub 2024 Jun 23. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38917944 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of liquid biopsy in breast cancer: Redefining the landscape of non-invasive precision oncology.J Liq Biopsy. 2025 May 21;8:100299. doi: 10.1016/j.jlb.2025.100299. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Liq Biopsy. 2025. PMID: 40521566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiplex detection of ten ESR1 mutations and AKT1 E17K in breast cancer using digital PCR.J Liq Biopsy. 2024 Mar 30;5:100154. doi: 10.1016/j.jlb.2024.100154. eCollection 2024 Sep. J Liq Biopsy. 2024. PMID: 40027941 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-free tumor DNA analysis in advanced or metastatic breast cancer patients: mutation frequencies, testing intention, and clinical impact.Precis Clin Med. 2024 Dec 24;8(1):pbae034. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbae034. eCollection 2025 Mar. Precis Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39839709 Free PMC article.
-
The Application of Circulating Tumour DNA (ctDNA) in the Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment Monitoring of Gynaecological and Breast Cancers (Review).Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 May 21;15(10):1289. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15101289. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40428282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen-Receptor Loss and ESR1 Mutation in Estrogen-Receptor-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer and the Effect on Overall Survival.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 30;16(17):3025. doi: 10.3390/cancers16173025. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Norton SE, Norton SE, Lechner JM, Williams T, Fernando MR. A stabilizing reagent prevents cell-free DNA contamination by cellular DNA in plasma during blood sample storage and shipping as determined by digital PCR. Clin Biochem (2013) 46(15):1561–5. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2013.06.002 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lim E, Metzger-Filho O, Winer EP. The natural history of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Oncol (Williston Park) (2012) 26(8):688–94, 696. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

