Robotic bronchoscopy in diagnosing lung cancer-the evidence, tips and tricks: a clinical practice review
- PMID: 37675302
- PMCID: PMC10477625
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-22-3078
Robotic bronchoscopy in diagnosing lung cancer-the evidence, tips and tricks: a clinical practice review
Abstract
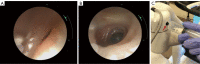
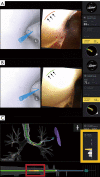
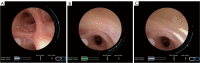
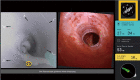
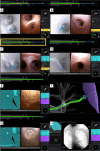
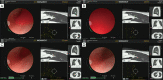
The development of robotic-assisted bronchoscopy has empowered bronchoscopists to access the periphery of the lung with more confidence and promising accuracy. This is due in large to the superior maneuverability, further reach, and stability of these technologies. Despite the advantages of robotic bronchoscopy, there are some drawbacks to using these technologies, such as the loss of tactile feedback, the need to overcome computed tomography (CT)-to-body divergence, and the potential for overreliance on the navigation software. There are currently two robotic bronchoscopy platforms on the US market, the MonarchTM Platform by Auris Health© (Redwood City, CA, USA) and the IonTM endoluminal robotic bronchoscopy platform by Intuitive Surgical© (Sunnyvale, CA, USA). In this clinical practice review, we highlight the evidence and strategies for successful clinical use of both robotic bronchoscopy platforms for pulmonary lesion sampling. Specifically, we will review pre-procedural considerations, such as procedural mapping, room set-up and anesthesia considerations. We will also review the technical aspects of using the robotic bronchoscopy platforms, such as how to compensate for the loss of tactile feedback, optimize visualization, use of ancillary technology to accommodate for CT-to-body divergence, employ best practices for sampling techniques, and utilize information from rapid on-site evaluation (ROSE) to aid in improving diagnostic yield.
Keywords: Robotic bronchoscopy; lung cancer; navigational bronchoscopy; pulmonary nodules.
2023 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-22-3078/coif). The series “Lung Cancer Management—The Next Decade” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. EH receives consulting fees from Intuitive, Olympus, and Biodesix. SM receives consulting fees from Olympus, Boston Scientific, Pinnacle Biologics, Johnson and Johnson, ERBE, Biodesix and Cook Inc. for developing and delivering educational events. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
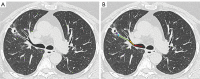
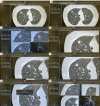
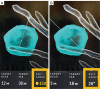
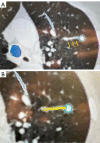
Figures


References
-
- Wahidi MM, Govert JA, Goudar RK, et al. Evidence for the treatment of patients with pulmonary nodules: when is it lung cancer?: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd edition). Chest 2007;132:94S-107S. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
