Immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: from current perspectives to future treatments-a systematic review
- PMID: 37675322
- PMCID: PMC10477621
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-22-4218
Immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: from current perspectives to future treatments-a systematic review
Abstract
Background: The introduction of immunotherapy in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has resulted in a radical change in patients' treatment responses and survival rates. The increased percentage of long survivors, improved toxicity profiles compared to chemotherapy, and the possible applications for different NSCLC scenarios, have led to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) becoming the cornerstone of NSCLC treatment. Therefore, the objective of this review is to describe the current and future perspectives of NSCLC treatment.
Methods: A systematic review according to the PRISMA criteria has been performed based on clinical trials with immunotherapy in NSCLC from the start of these treatments until June 2022.
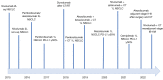
Results: The use of ICIs is widespread across both first- and second-line treatments with anti-PD-1, anti-PD-L1, and anti-CTLA-4 drugs. New indications for immunotherapy in NSCLC have focused on adjuvant (atezolizumab) and neoadjuvant (nivolumab), with ICIs now present in all stages of NSCLC treatment. Given the promising results seen in clinical trials, new ICIs [anti- lymphocyte activation gene-3 (LAG-3) or IDO1] currently under development, will soon be used as standard treatment for NSCLC.
Conclusions: Immunotherapy is the mainstay of NSCLC treatment in all stages, including adjuvant, neoadjuvant and advanced tumors. The development of new molecules will revolutionize the treatment of NSCLC in the coming years.
Keywords: anti-CTLA-4; anti-PD-1; anti-PD-L1; immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs); non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
2023 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-22-4218/coif). JPMG serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Annals of Translational Medicine from June 2022 to May 2024. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Comment in
-
New developments and updates in non-small cell lung cancer and immunotherapy: adjuvant, neoadjuvant and advanced stages.Ann Transl Med. 2023 Dec 20;11(12):423. doi: 10.21037/atm-23-1854. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Ann Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 38213799 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
