Extracorporeal blood purification in patients with liver failure: Considerations for the low-and-middle income countries of Latin America
- PMID: 37675369
- PMCID: PMC10479632
- DOI: 10.3389/fneph.2023.938710
Extracorporeal blood purification in patients with liver failure: Considerations for the low-and-middle income countries of Latin America
Abstract
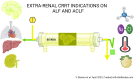
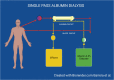
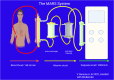
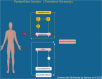
Severe liver failure is common in Low-and-Medium Income Countries (LMIC) and is associated with a high morbidity, mortality and represents an important burden to the healthcare system. In its most severe state, liver failure is a medical emergency, that requires supportive care until either the liver recovers or a liver transplant is performed. Frequently the patient requires intensive support until their liver recovers or they receive a liver transplant. Extracorporeal blood purification techniques can be employed as a strategy for bridging to transplantation or recovery. The most common type of extracorporeal support provided to these patients is kidney replacement therapy (KRT), as acute kidney injury is very common in these patients and KRT devices more readily available. However, because most of the substances that the liver clears are lipophilic and albumin-bound, they are not cleared effectively by KRT. Hence, there has been much effort in developing devices that more closely resemble the clearance function of the liver. This article provides a review of various non-biologic extracorporeal liver support devices that can be used to support these patients, and our perspective keeping in mind the needs and unique challenges present in the LMIC of Latin America.
Keywords: CRRT - continuous renal replacement therapy; acute liver failure; acute liver failure (ALF); continuous renal replacement therapy; extra-renal; extracorporeal liver assist device; extracorporeal liver support devices; extrarenal.
Copyright © 2023 Villanueva, Barrera Amorós, Castillo Echeverria, Budar-Fernández, Salas Nolasco, Juncos and Rizo-Topete.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liver replacement therapy with extracorporeal blood purification techniques current knowledge and future directions.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Jun 16;11(17):3932-3948. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i17.3932. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 37388799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracorporeal renal and liver support in pediatric acute liver failure.Pediatr Nephrol. 2021 May;36(5):1119-1128. doi: 10.1007/s00467-020-04613-4. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Pediatr Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 32500250 Review.
-
Combination of continuous renal replacement therapies (CRRT) and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) for advanced cardiac patients.Ren Fail. 2003 Mar;25(2):183-93. doi: 10.1081/jdi-120018719. Ren Fail. 2003. PMID: 12739825
-
Liver support in fulminant liver failure after hemorrhagic shock.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2003 Sep 15;115(15-16):595-8. doi: 10.1007/BF03040455. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2003. PMID: 14531174
-
Kidney Support in Children using an Ultrafiltration Device: A Multicenter, Retrospective Study.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019 Oct 7;14(10):1432-1440. doi: 10.2215/CJN.03240319. Epub 2019 Aug 28. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31462396 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Asociation for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) , in: Chronic Liver disease Evolution and Registry for Event and Decompensation (CLEARED) global consortium study, Presented at the Liver Meeting (AASLD, 11/08/2022.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials