The circadian clock ticks in plant stress responses
- PMID: 37676516
- PMCID: PMC10441891
- DOI: 10.1007/s44154-022-00040-7
The circadian clock ticks in plant stress responses
Abstract
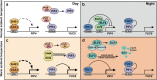
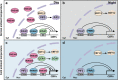
The circadian clock, a time-keeping mechanism, drives nearly 24-h self-sustaining rhythms at the physiological, cellular, and molecular levels, keeping them synchronized with the cyclic changes of environmental signals. The plant clock is sensitive to external and internal stress signals that act as timing cues to influence the circadian rhythms through input pathways of the circadian clock system. In order to cope with environmental stresses, many core oscillators are involved in defense while maintaining daily growth in various ways. Recent studies have shown that a hierarchical multi-oscillator network orchestrates the defense through rhythmic accumulation of gene transcripts, alternative splicing of mRNA precursors, modification and turnover of proteins, subcellular localization, stimuli-induced phase separation, and long-distance transport of proteins. This review summarizes the essential role of circadian core oscillators in response to stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana and crops, including daily and seasonal abiotic stresses (low or high temperature, drought, high salinity, and nutrition deficiency) and biotic stresses (pathogens and herbivorous insects). By integrating time-keeping mechanisms, circadian rhythms and stress resistance, we provide a temporal perspective for scientists to better understand plant environmental adaptation and breed high-quality crop germplasm for agricultural production.
Keywords: Circadian clock; Drought; Pathogen; Salinity; Temperature stress.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
X.X. is a member of the Editorial Board and was not involved in the journal’s review of, or decisions related to, this manuscript.
Figures



References
-
- Baek D, Kim WY, Cha JY, Park HJ, Shin G, Park J, Lim CJ, Chun HJ, Li N, Kim DH, Lee SY, Pardo JM, Kim MC, Yun DJ. The GIGANTEA-ENHANCED EM LEVEL complex enhances drought tolerance via regulation of abscisic acid synthesis. Plant Physiol. 2020;184:443–458. doi: 10.1104/pp.20.00779. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

