Oxidative addition of an alkyl halide to form a stable Cu(III) product
- PMID: 37676952
- PMCID: PMC10658983
- DOI: 10.1126/science.adg9232
Oxidative addition of an alkyl halide to form a stable Cu(III) product
Abstract
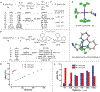
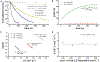
The step that cleaves the carbon-halogen bond in copper-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions remains ill defined because of the multiple redox manifolds available to copper and the instability of the high-valent copper product formed. We report the oxidative addition of α-haloacetonitrile to ionic and neutral copper(I) complexes to form previously elusive but here fully characterized copper(III) complexes. The stability of these complexes stems from the strong Cu-CF3 bond and the high barrier for C(CF3)-C(CH2CN) bond-forming reductive elimination. The mechanistic studies we performed suggest that oxidative addition to ionic and neutral copper(I) complexes proceeds by means of two different pathways: an SN2-type substitution to the ionic complex and a halogen-atom transfer to the neutral complex. We observed a pronounced ligand acceleration of the oxidative addition, which correlates with that observed in the copper-catalyzed couplings of azoles, amines, or alkynes with alkyl electrophiles.
Figures


References
-
- Beletskaya I, Cheprakov AV, Coord. Chem. Rev. 248, 2337–2364 (2004).
-
- Evano G, Blanchard N, Toumi M, Chem. Rev. 108, 3054–3131 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Monnier F, Taillefer M, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48, 6954–6971 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Bhunia S, Pawar GG, Kumar SV, Jiang Y, Ma D, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 16136–16179 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Cheng L-J, Mankad NP, Chem. Soc. Rev. 49, 8036–8064 (2020). - PubMed

