Modulation of the proteostasis network promotes tumor resistance to oncogenic KRAS inhibitors
- PMID: 37676964
- PMCID: PMC10720158
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abn4180
Modulation of the proteostasis network promotes tumor resistance to oncogenic KRAS inhibitors
Abstract
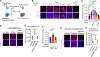
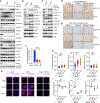
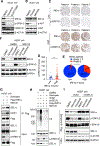
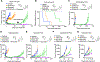
Despite substantial advances in targeting mutant KRAS, tumor resistance to KRAS inhibitors (KRASi) remains a major barrier to progress. Here, we report proteostasis reprogramming as a key convergence point of multiple KRASi-resistance mechanisms. Inactivation of oncogenic KRAS down-regulated both the heat shock response and the inositol-requiring enzyme 1α (IRE1α) branch of the unfolded protein response, causing severe proteostasis disturbances. However, IRE1α was selectively reactivated in an ER stress-independent manner in acquired KRASi-resistant tumors, restoring proteostasis. Oncogenic KRAS promoted IRE1α protein stability through extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)-dependent phosphorylation of IRE1α, leading to IRE1α disassociation from 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl reductase degradation (HRD1) E3-ligase. In KRASi-resistant tumors, both reactivated ERK and hyperactivated AKT restored IRE1α phosphorylation and stability. Suppression of IRE1α overcame resistance to KRASi. This study reveals a druggable mechanism that leads to proteostasis reprogramming and facilitates KRASi resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
M.F.R. receives research funding from Pfizer and Genentech. M.F.R. is a consultant and receives consulting fees from: Novartis, Seagen, Macrogenics, and AstraZeneca. M.F.R. is the Principal Investigator of the clinical trial
Figures




Comment in
-
Rewired proteostasis in KRAS inhibitor resistance.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023 Nov;22(11):871. doi: 10.1038/d41573-023-00155-0. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023. PMID: 37758873 No abstract available.
-
Addicted to proteostasis: How KRAS-driven cancers acquire resistance to clinical KRAS inhibitors.Cell Chem Biol. 2023 Nov 16;30(11):1334-1336. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.10.007. Cell Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37977128
References
-
- Scheidig AJ, Burmester C, Goody RS, The pre-hydrolysis state of p21(ras) in complex with GTP: new insights into the role of water molecules in the GTP hydrolysis reaction of ras-like proteins. Structure 7, 1311–1324 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Scheffzek K. et al. , The Ras-RasGAP complex: structural basis for GTPase activation and its loss in oncogenic Ras mutants. Science 277, 333–338 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Bollag G, McCormick F, Differential regulation of rasGAP and neurofibromatosis gene product activities. Nature 351, 576–579 (1991). - PubMed
-
- McGrath JP, Capon DJ, Goeddel DV, Levinson AD, Comparative biochemical properties of normal and activated human ras p21 protein. Nature 310, 644–649 (1984). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U24 CA210954/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA224065/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA224081/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA117969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA228304/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD008188/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA126752/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK115454/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS117668/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA196941/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA195651/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA248478/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL146642/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD007857/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA272744/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD100535/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD028671/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056338/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD025251/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM130838/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR024574/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA270240/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA214793/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK060445/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM142143/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA215591/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA186784/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

