Don't hold PAT: watch for and correct oximetry artifact
- PMID: 37677072
- PMCID: PMC10692927
- DOI: 10.5664/jcsm.10800
Don't hold PAT: watch for and correct oximetry artifact
Abstract
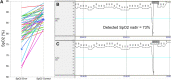
This study evaluated the accuracy of the algorithmic oxygen saturation (SpO2) nadir detection of WatchPAT (Zoll/Itamar, Caesarea, Israel) compared with visual inspection in a real-world setting. SpO2 tracings for 209 consecutive adult WatchPAT recordings were reviewed for SpO2 artifact, with erroneous SpO2 data removed manually. Error rates for SpO2 minima were determined across all studies, and relationships between correct and erroneous studies examined. The overall error rate for SpO2 nadir was 22.5%. Erroneous studies had overall less time spent at SpO2 ≤ 88%, higher true SpO2 nadir, lower mean body mass index, and greater artifact time; however, these variables were not associated with the magnitude of discrepancy between manual and algorithmically derived SpO2 minima. These data demonstrate that SpO2 nadir determined by WatchPAT algorithms should not be considered universally accurate. Like other home sleep apnea tests, visual inspection and manual correction of the study data are often required to derive accurate clinical results.
Citation: Plante DT, Rumble ME. Don't hold PAT: watch for and correct oximetry artifact. J Clin Sleep Med. 2023;19(12):2113-2116.
Keywords: WatchPAT; hypoxemia; sleep apnea; tonometry.
© 2023 American Academy of Sleep Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Both authors have reviewed and approved the manuscript. Work for this study was performed at the University of Wisconsin-Madison and was not funded. Dr. Plante has received grant support from the National Institute on Aging (NIA), National Institute of Nursing Research (NINR), National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), American Sleep Medicine Foundation, the Brain and Behavior Research Foundation, Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation, Alzheimer’s Association, and the University of Illinois at Chicago Occupational and Environmental Health and Safety Education and Research Center/National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health; has served as a consultant for Teva Australia, Harmony Biosciences, Aditum Bio LLC, and Jazz Pharmaceuticals; and served on medical advisory boards for Jazz Pharmaceuticals and Alkermes, all unrelated to the current study. Dr. Rumble has received grant support from Merck, unrelated to the current study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparative study of accuracy in major adaptive filters for motion artifact removal in sleep apnea tests.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2024 Mar;62(3):829-842. doi: 10.1007/s11517-023-02979-9. Epub 2023 Dec 5. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2024. PMID: 38052880 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral arterial tonometry, oximetry and actigraphy for ambulatory recording of sleep apnea.Physiol Meas. 2004 Aug;25(4):1025-36. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/25/4/019. Physiol Meas. 2004. PMID: 15382839
-
The Impact of Averaging Window Length on the"Desaturation Indexes during Overnight Pulse Oximetry at High-Altitude".Sleep. 2015 Aug 1;38(8):1331-4. doi: 10.5665/sleep.4920. Sleep. 2015. PMID: 25581919 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep Study and Oximetry Parameters for Predicting Postoperative Complications in Patients With OSA.Chest. 2019 Apr;155(4):855-867. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.09.030. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Chest. 2019. PMID: 30359618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
State of home sleep studies.Clin Chest Med. 2003 Jun;24(2):283-95. doi: 10.1016/s0272-5231(03)00018-2. Clin Chest Med. 2003. PMID: 12800784 Review.
References
-
- Poets CF , Stebbens VA . Detection of movement artifact in recorded pulse oximeter saturation . Eur J Pediatr. 1997. ; 156 ( 10 ): 808 – 811 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

