Epivolve: A Protocol for Site-Directed Antibodies
- PMID: 37679640
- PMCID: PMC10568616
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3381-6_29
Epivolve: A Protocol for Site-Directed Antibodies
Abstract
Researchers can often successfully generate antibodies to predicted epitopes. Especially when the epitopes are on the surface of a protein or in a hydrophilic loop. But it is difficult to direct recombinant antibodies to bind either to- or near a specific amino acid on a protein or peptide. We have developed a unique immune-targeting strategy, that we call "Epivolve," that enables us to make site-specific antibodies (Abs). Epivolve technology leverages a highly immunogenic modified amino acid that acts as a "pseudo-hapten" immuno-target and takes advantage of Ab affinity maturation technologies to make high-affinity site-specific antibodies. Epivolve functions by the evolution of an Ab paratope to either synonymous or especially non-synonymous amino acid (aa) binding. Here we describe the use of Epivolve technology in phage display and the protocols for developing site-specific antibodies.
Keywords: Antibody; Biopanning; Epivolve; Phage display; Site-directed; Site-specific.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Figures
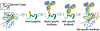

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

