ILC1-derived IFN-γ regulates macrophage activation in colon cancer
- PMID: 37679802
- PMCID: PMC10486120
- DOI: 10.1186/s13062-023-00401-w
ILC1-derived IFN-γ regulates macrophage activation in colon cancer
Erratum in
-
Correction: ILC1-derived IFN-γ regulates macrophage activation in colon cancer.Biol Direct. 2023 Dec 4;18(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s13062-023-00432-3. Biol Direct. 2023. PMID: 38049857 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are an important subset of innate immune cells in the tumor microenvironment, and they are pivotal regulators of tumor-promoting inflammation and tumor progression. Evidence has proven that TAM numbers are substantially increased in cancers, and most of these TAMs are polarized toward the alternatively activated M2 phenotype; Thus, these TAMs strongly promote the progression of cancer diseases. Type 1 innate lymphocytes (ILC1s) are present in high numbers in intestinal tissues and are characterized by the expression of the transcription factor T-bet and the secretion of interferon (IFN)-γ, which can promote macrophages to polarize toward the classically activated antitumor M1 phenotype. However, the relationship between these two cell subsets in colon cancer remains unclear.
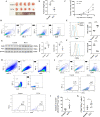
Methods: Flow cytometry was used to determine the percentages of M1-like macrophages, M2-like macrophages and ILC1s in colon cancer tissues and paracancerous healthy colon tissues in the AOM/DSS-induced mouse model of colon cancer. Furthermore, ILC1s were isolated and bone marrow-derived macrophages were generated to analyze the crosstalk that occurred between these cells when cocultured in vitro. Moreover, ILC1s were adoptively transferred or inhibited in vivo to explore the effects of ILC1s on tumor-infiltrating macrophages and tumor growth.
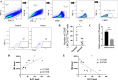
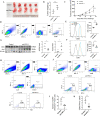
Results: We found that the percentages of M1-like macrophages and ILC1s were decreased in colon cancer tissues, and these populations were positively correlated. ILC1s promoted the polarization of macrophages toward the classically activated M1-like phenotype in vitro, and this effect could be blocked by an anti-IFN-γ antibody. The in vivo results showed that the administration of the Group 1 innate lymphocyte-blocking anti-NK1.1 antibody decreased the number of M1-like macrophages in the tumor tissues of MC38 tumor-bearing mice and promoted tumor growth, and adoptive transfer of ILC1s inhibited tumors and increased the percentage of M1-like macrophages in MC38 tumor-bearing mice.
Conclusions: Our studies preliminarily prove for the first time that ILC1s promote the activation of M1-like macrophages by secreting IFN-γ and inhibit the progression of colon cancer, which may provide insight into immunotherapeutic approaches for colon cancer.
Keywords: Colon cancer; Group 1 innate lymphocytes; IFN-γ; M1 macrophage; Tumor-associated macrophage.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

