Correlation of extended Martin/Hopkins equation with a direct homogeneous assay in assessing low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients with hypertriglyceridemia
- PMID: 37679962
- PMCID: PMC10623527
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.24963
Correlation of extended Martin/Hopkins equation with a direct homogeneous assay in assessing low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients with hypertriglyceridemia
Abstract
Background: The Friedewald or Martin/Hopkins equation is widely used to estimate low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) at triglyceride (TG) levels <400 mg/dL. In this study, we aimed to validate the recently developed Sampson and extended Martin/Hopkins equations intended for use in patients with TG levels up to 800 mg/dL by comparing them to a direct homogenous assay.
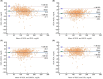
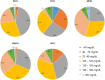
Methods: In total, 8676 participants with serum TG levels <800 mg/dL were enrolled in this study. LDL-C was directly measured using Abbott homogeneous assay (DLDL) and estimated using the Friedewald (FLDL), Martin/Hopkins (MLDL), extended Martin/Hopkins (EMLDL), and Sampson equations (SLDL). The overall concordance between the DLDL and LDL-C estimates was calculated. The performance of the four equations was also compared using Bland-Altman plots and mean absolute difference (MAD).
Results: The EMLDL was more accurate than other LDL-C equations particularly for patients with TG≥400 mg/dL (MAD = 10.43; vs. FLDL: MAD = 21.1; vs. SLDL: MAD 11.62). The overall concordance of FLDL, MLDL, EMLDL, and SLDL with DLDL in TG values ranging from 200 to 799 mg/dL were 52.2, 70.5, 71.6, and 65.7%, respectively (p < 0.001), demonstrating the EMLDL as the most optimal estimation method, particularly for high TG levels (≥200 mg/dL).
Conclusion: Both the original and extended Martin/Hopkins method are optimal in estimating LDL-C levels in clinical laboratories using the Abbott analyzer in patients with TG levels of 200-399 and 400-799 mg/dL, respectively. Meanwhile, caution is need that considerable underestimation of Friedewald and Sampson equation could lead to undertreatment in hypertriglyceridemia.
Keywords: Friedewald equation; Sampson equation; extended Martin/Hopkins equation; hypertriglyceridemia; low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
© 2023 The Author. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Who.int [homepage on the internet] . World Health Organization: Cardiovascular diseases: fact sheet. [Accessed 2023 April 15]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news‐room/fact‐sheets/detail/cardiovascular‐diseases...
-
- Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;139(25):e1082‐e1143. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sathiyakumar V, Park J, Golozar A, et al. Fasting versus nonfasting and low‐density lipoprotein cholesterol accuracy. Circulation. 2018;137(1):10‐19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

