A systematic review evaluating the effectiveness of exercise training on physical condition in prostate cancer patients undergoing androgen deprivation therapy
- PMID: 37680229
- PMCID: PMC10481197
- DOI: 10.21037/tau-23-272
A systematic review evaluating the effectiveness of exercise training on physical condition in prostate cancer patients undergoing androgen deprivation therapy
Abstract
Background: Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) is an effective prostate cancer (PCa) treatment strategy that can curb the development or progression of the disease. This review aimed to examine and summarize available systematic reviews/meta-analyses (SRs/MAs) of exercise training on physical condition of PCa patients undergoing ADT.
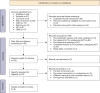
Methods: A comprehensive search of 8 databases was conducted for relevant literature published before April 25, 2022 with the language restrictions of Chinese and English. Two reviewers independently assessed the methodological quality, risk of bias, reporting quality, and evidence quality of the included SRs/MAs using a range of evaluation tools, including A Measurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews (AMSTAR) 2, Risk of Bias in Systematic Reviews (ROBIS), the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA), and Grades of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE).
Results: This review included 8 SRs/MAs which included a total of 94 studies. Ultimately, A total of 51 outcomes was included, regarding 11 different outcome categories. The AMSTAR-2 tool showed that 3 SRs/MAs had moderate methodological quality, 4 SRs/MAs had very low quality, and the remaining 1 had low quality. According to the ROBIS scale, 3 SRs/MAs had a high risk of bias. The PRISMA checklist showed that the primary reporting faults were protocol registration and funding source. The GRADE system was used to analyze the evidence quality of the 51 outcomes, and no high-quality evidence was found. However, moderate-quality evidence indicated that exercise training may improve body composition [by lowering body fat mass (BFM) and body fat rate (BFR)], muscular strength, and quality of life (QoL) in PCa patients undergoing ADT. Low-quality evidence demonstrated that exercise training could improve such symptoms as fatigue, depression, sexual function, and cardiometabolic changes.
Conclusions: Available evidence suggests that exercise training may be used as an adjuvant treatment for PCa patients undergoing ADT to improve several aspects of general health. Studies with more rigorous designs and larger sample sizes are needed to support our findings with more robust evidence.
Keywords: Exercise; prostate cancer (PCa); systematic review (SR).
2023 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tau.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tau-23-272/coif). HK received support for attending a conference from Janssen Pharmaceuticals (2022), participated in an advisory board meeting: Ferring Pharmaceuticals (2021), Janssen Pharmaceuticals (2022) and received honorarium from Recordati for a presentation (2021). The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness and safety of manual therapy for knee osteoarthritis: An overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses.Front Public Health. 2023 Feb 24;11:1081238. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1081238. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36908468 Free PMC article.
-
Benefits and Safety of Chinese Herbal Medicine in Treating Psoriasis: An Overview of Systematic Reviews.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 1;12:680172. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.680172. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34276371 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Acupuncture in the Treatment of Essential Hypertension: An Overview of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses.Cardiovasc Ther. 2023 Apr 18;2023:2722727. doi: 10.1155/2023/2722727. eCollection 2023. Cardiovasc Ther. 2023. PMID: 37113506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tai Chi for improving balance and reducing falls: An overview of 14 systematic reviews.Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2020 Nov;63(6):505-517. doi: 10.1016/j.rehab.2019.12.008. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2020. PMID: 31981834
-
Evidence quality assessment of sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate injection intervention coronary heart disease angina pectoris: An overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Nov 3;102(44):e35509. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035509. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37933033 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous