Aggressive chronic lymphocytic leukemia masked by extensive marrow fibrosis
- PMID: 37680324
- PMCID: PMC10480308
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lrr.2023.100390
Aggressive chronic lymphocytic leukemia masked by extensive marrow fibrosis
Abstract
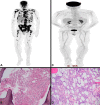
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is one of the most common B-cell leukemias, occurring because of abnormal proliferation of non-functional B-lymphocytes. Progressive disease is commonly complicated by anemia, thrombocytopenia, infections as well as secondary malignancies. Bone marrow fibrosis is infrequently co-occurred along with CLL. Although multiple explanations have been proposed for this association, the etiology remains unclear in most cases. Bone marrow fibrosis occurring as a complication of CLL itself, however, is a rare entity. We present an uncommon case of a patient initially diagnosed with primary myelofibrosis but later revealed to have aggressive CLL leading to bone marrow fibrosis upon re-evaluation. Treatment for CLL resolved the bone marrow fibrosis completely, confirming our suspicion of fibrosis being secondary to CLL. This sheds light on the importance of understanding the etiology of bone marrow fibrosis in patients with CLL owing to its therapeutic implications. The utility of bone marrow biopsy in not only helping understand the etiology of the fibrosis but also providing prognostic information merits reconsideration of performing it in all cases of CLL.
Keywords: B-Cell; Bone marrow examination; Bone marrow fibrosis; Leukemia; Primary myelofibrosis.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Talha Badar reports receiving honoraria/ serving in an advisory board for Pfizer-hematology and Oncology. Received Mayo Clinic Cancer Center Support Grant (CCSG) (P30 CA015083)
Figures
Similar articles
-
Significance of bone marrow reticulin fibrosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia at diagnosis: a study of 176 patients with prognostic implications.Cancer. 2013 May 15;119(10):1853-9. doi: 10.1002/cncr.27930. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23423815
-
Relationship between the expression of CD25 and CD69 on the surface of lymphocytes T and B from peripheral blood and bone marrow of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and established prognostic factors of this disease.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2018 Jul;27(7):987-999. doi: 10.17219/acem/74437. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 29893517
-
Monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis in the bone marrow: revisiting the criteria for chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma.Hum Pathol. 2022 Jul;125:108-116. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2022.04.010. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Hum Pathol. 2022. PMID: 35472399
-
Rituximab: a review of its use in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.Drugs. 2003;63(8):803-43. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00005. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12662126 Review.
-
Role of microRNAs in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Pathogenesis.Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(2):282-297. doi: 10.2174/0929867326666190911114842. Curr Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31544709 Review.
References
-
- Tadmor T., Shvidel L., Aviv A., Ruchlemer R., Bairey O., Yuklea M., et al. Significance of bone marrow reticulin fibrosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia at diagnosis: a study of 176 patients with prognostic implications. Cancer. 2013;119:1853–1859. - PubMed
-
- Kimura A., Hyodo H., Nakata Y., Kuramoto A. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia associated with bone marrow fibrosis: possible role of interleukin 1 alpha in the pathogenesis. Am. J. Hematol. 1993;43:47–50. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources