Comparative Transcriptomic Analyses of a Vero Cell Line in Suspension versus Adherent Culture Conditions
- PMID: 37680537
- PMCID: PMC10482560
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/9364689
Comparative Transcriptomic Analyses of a Vero Cell Line in Suspension versus Adherent Culture Conditions
Abstract
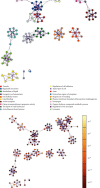
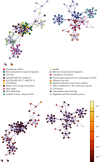
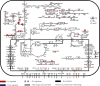
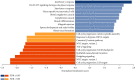
The Vero cell line is the most used continuous cell line for viral vaccine manufacturing. Its anchorage-dependent use renders scaling up challenging and operations very labor-intensive which affects cost effectiveness. Thus, efforts to adapt Vero cells to suspension cultures have been invested, but hurdles such as the long doubling time and low cell viability remain to be addressed. In this study, building on the recently published Vero cell line annotated genome, a functional genomics analysis of the Vero cells adapted to suspension is performed to better understand the genetic and phenotypic switches at play during the adaptation of Vero cells from anchorage-dependent to suspension cultures. Results show downregulation of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) pathway, highlighting the dissociation between the adaptation to suspension process and EMT. Surprisingly, an upregulation of cell adhesion components is observed, notably the CDH18 gene, the cytoskeleton pathway, and the extracellular pathway. Moreover, a downregulation of the glycolytic pathway is balanced by an upregulation of the asparagine metabolism pathway, promoting cell adaptation to nutrient deprivation. A downregulation of the adherens junctions and the folate pathways alongside with the FYN gene are possible explanations behind the currently observed low-cell viability and long doubling time.
Copyright © 2023 Marie-Angélique Sène et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no financial or nonfinancial competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- COVID-19 vaccine tracker and landscape. https://www.who.int/teams/blueprint/covid-19/covid-19-vaccine-tracker-an... .
-
- Madeline B., Ribaud S., Xenopoulos A., Simler J., Schwamborn K., Léon A. Culturing a duck es-derived cell line in single-use bioreactors: a rapid, efficient, and cost-effective vaccine manufacturing system based on suspension culture. Bioprocess International . 2015;13(3):26–33.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

