Delphi: A Democratic and Cost-Effective Method of Consensus Generation in Transplantation
- PMID: 37680647
- PMCID: PMC10481336
- DOI: 10.3389/ti.2023.11589
Delphi: A Democratic and Cost-Effective Method of Consensus Generation in Transplantation
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Delphi: A Democratic and Cost-Effective Method of Consensus Generation in Transplantation.Transpl Int. 2023 Oct 16;36:12046. doi: 10.3389/ti.2023.12046. eCollection 2023. Transpl Int. 2023. PMID: 37908677 Free PMC article.
Abstract
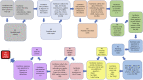
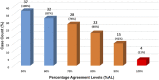
The Thrombotic Microangiopathy Banff Working Group (TMA-BWG) was formed in 2015 to survey current practices and develop minimum diagnostic criteria (MDC) for renal transplant TMA (Tx-TMA). To generate consensus among pathologists and nephrologists, the TMA BWG designed a 3-Phase study. Phase I of the study is presented here. Using the Delphi methodology, 23 panelists with >3 years of diagnostic experience with Tx-TMA pathology listed their MDC suggesting light, immunofluorescence, and electron microscopy lesions, clinical and laboratory information, and differential diagnoses. Nine rounds (R) of consensus resulted in MDC validated during two Rs using online evaluation of whole slide digital images of 37 biopsies (28 TMA, 9 non-TMA). Starting with 338 criteria the process resulted in 24 criteria and 8 differential diagnoses including 18 pathologic, 2 clinical, and 4 laboratory criteria. Results show that 3/4 of the panelists agreed on the diagnosis of 3/4 of cases. The process also allowed definition refinement for 4 light and 4 electron microscopy lesions. For the first time in Banff classification, the Delphi methodology was used to generate consensus. The study shows that Delphi is a democratic and cost-effective method allowing rapid consensus generation among numerous physicians dealing with large number of criteria in transplantation.
Keywords: Banff; Delphi; kidney; thrombotic microangiopathy; transplantation.
Copyright © 2023 Afrouzian, Kozakowski, Liapis, Broecker, Truong, Avila-Casado, Regele, Seshan, Ambruzs, Farris, Buob, Chander, Cheraghvandi, Clahsen-van Groningen, de Almeida Araujo, Ertoy Baydar, Formby, Galesic Ljubanovic, Herrera Hernandez, Honsova, Mohamed, Ozluk, Rabant, Royal, Stevenson, Toniolo and Taheri.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Solez K, Axelsen RA, Benediktsson H, Burdick JF, Cohen AH, Colvin RB, et al. International Standardization of Criteria for the Histologic Diagnosis of Renal Allograft Rejection: The Banff Working Classification of Kidney Transplant Pathology. Kidney Int (1993) 44:411–22. 10.1038/ki.1993.259 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Haas M, Loupy A, Lefaucheur C, Roufosse C, Glotz D, Seron D, et al. The Banff 2017 Kidney Meeting Report: Revised Diagnostic Criteria for Chronic Active T Cell-Mediated Rejection, Antibody-Mediated Rejection, and Prospects for Integrative Endpoints for Next-Generation Clinical Trials. Am J Transpl (2018) 18:293–307. 10.1111/ajt.14625 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

