Involvement of Nrf2, JAK and COX pathways in acetaminophen-induced nephropathy: Role of some antioxidants
- PMID: 37680754
- PMCID: PMC10480313
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.101752
Involvement of Nrf2, JAK and COX pathways in acetaminophen-induced nephropathy: Role of some antioxidants
Abstract
Objectives: Acetaminophen (APAP)-induced nephrotoxicity is detrimental consequence for which there has not been a standardized therapeutic regimen. Although, N-acetylcysteine (NAC) is a well-known antidote used in APAP-induced hepatotoxicity, its benefit in nephrotoxicity caused by APAP is almost lacking. This study aimed to compare the possible protective effect of thymoquinone (TQ), curcumin (CR), and α-lipoic acid (α-LA), either in solo or in combination regimens with that of NAC against APAP-induced renal injury.
Design and method: Rats were divided into nine groups; control group, APAP intoxicated group (1000 mg/kg; orally), and the remaining seven groups received, in addition to APAP, oral doses of NAC, TQ, CR, α-LA, CR plus TQ, TQ plus α-LA, or CR plus α-LA. The first dose of the aforementioned antioxidants was given 24 h before APAP, and then the second dose was given 2 h after APAP, whereas the last dose was given 10 h after administration of APAP.
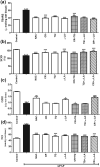
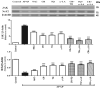
Results: Treatment with APAP elevated kidney markers like serum uric acid, urea, and creatinine. In addition, it increased the serum level of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1beta (IL-1β) and thiobarbituric acid reactive species (TBARS). Also, the protein expression of renal janus kinase (JAK) and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 were all upregulated by APAP. In contrast, the expression of Nrf2 and the renal levels of superoxide dismutase and glutathione were downregulated. Treatment with the indicated natural antioxidants resulted in amelioration of the aberrated parameters through exhibiting anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and free radical-scavenging effects with a variable degree.
Conclusion: The combined administration of CR and TQ exerted the most potent protection against APAP-induced nephrotoxicity through its anti-inflammatory and free radical-scavenging effects (antioxidant) which were comparable to that of NAC-treatment.
Keywords: Acetaminophen; COX; Curcumin; JAK; N-acetylcysteine; Nrf2; Thymoquinone; α-Lipoic acid.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Al-Zahrani M.H., Balgoon M.J., El-Sawi N.M., et al. A biochemical, theoretical and immunohistochemical study comparing the therapeutic efficacy of curcumin and taurine on T-2 toxin induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023;10:1172403. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1172403. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aycan, İ. Ö., O. Tokgöz, A. Tüfek, et al., 2015. The use of thymoquinone in nephrotoxicity related to acetaminophen. International Journal of Surgery. 13, 33-37. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

