The relationship between CMV reactivation, anti-cytokine treatment and mortality in critical COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 37680795
- PMCID: PMC10480725
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.39.5.7301
The relationship between CMV reactivation, anti-cytokine treatment and mortality in critical COVID-19 patients
Abstract
Objective: To examine the use of anti-cytokine treatment in critical COVID-19 patients and their association with the frequency of CMV cases, viral load level, and mortality in these patients.
Methods: This is a retrospective study. A total of 170 critical and/or intensive care patients with COVID-19 admitted to Hisar Hospital Intercontinental from March 15, 2020, to December 31, 2021 were divided into the use of anti-cytokine treatment group and the no anti-cytokine treatment group. Furthermore, the relationship between CMV reactivation, mortality and anti-cytokine treatment in patients was also examined.
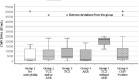
Results: A total of 170 critical COVID-19 patients were included in the study, three of them were excluded. One hundred sixty seven were included in the study of which 38 (22.7%) were found to be CMV DNA positive. As an anti-cytokine treatment, it was observed that tocilizumab was used in 53 patients, anakinra was used in 27 patients, and no anti-cytokine treatment was used in 77 patients. CMV positivity in patients treated with anti-cytokines (31.11%) was found to be significantly higher than in patients who were not treated with it (16.88%) (p:0.033). Furthermore, it was determined that anti-cytokine treatment significantly decreased mortality (p: 0.003) and that there was no significant relationship between CMV reactivation and mortality (p: 0.399).
Conclusion: Even though CMV reactivation was high in critical COVID-19 patients who received anti-cytokine treatment, decrease in mortality were observed with early diagnosis and effective treatment. Therefore, CMV infection should be considered in patients receiving immunosuppressive treatment.Clinical Trial Registration: HisarIH-101/NCT05419206.
Keywords: Anakinra; Anti-cytokine treatment; COVID-19; Cytomegalovirus (CMV); Mortality; Tocilizumab.
Copyright: © Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests: None.
Figures
References
-
- Niitsu T, Shiroyama T, Hirata H, Noda Y, Adachi Y, Enomoto T, et al. Cytomegalovirus infection in critically ill patients with COVID-19. J Infect. 2021;83(4):496–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2021.07.004. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cakiroglu B, Kaya C, Kilic HH, Aksoy SH, Gozukucuk R. Did COVID-19 area change our urology practice:A retrospective analysis. Urologia. 2022;89(2):149–152. doi: 10.1177/03915603211001681. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials