Clinical and anatomical analysis of the epileptogenic spread patterns in focal cortical dysplasia patients
- PMID: 37680931
- PMCID: PMC10481808
- DOI: 10.25259/SNI_210_2023
Clinical and anatomical analysis of the epileptogenic spread patterns in focal cortical dysplasia patients
Abstract
Background: Focal cortical dysplasia (FCD) is one of the main causes of intractable epilepsy, which is amendable by surgery. During the surgical management of FCD, the understanding of its epileptogenic foci, interconnections, and spreading pathways is crucial for attaining a good postoperative seizure free outcome.
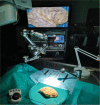
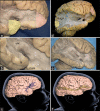
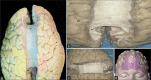
Methods: We retrospectively evaluated 54 FCD patients operated in Federal Center of Neurosurgery, Tyumen, Russia. The electroencephalogram findings were correlated to the involved brain anatomical areas. Subsequently, we analyzed the main white matter tracts implicated during the epileptogenic spreading in some representative cases. We prepared 10 human hemispheres using Klinger's method and dissected them through the fiber dissection technique.
Results: The clinical results were displayed and the main white matter tracts implicated in the seizure spread were described in 10 patients. Respective FCD foci, interconnections, and ectopic epileptogenic areas in each patient were discussed.
Conclusion: A strong understanding of the main implicated tracts in epileptogenic spread in FCD patient remains cardinal for neurosurgeons dealing with epilepsy. To achieve meaningful seizure freedom, despite the focal lesion resection, the interconnections and tracts should be understood and somehow disconnected to stop the spreading.
Keywords: Epilepsy; Focal dysplasia; Seizure spreading; White matter tract.
Copyright: © 2023 Surgical Neurology International.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Gray-matter-specific MR imaging improves the detection of epileptogenic zones in focal cortical dysplasia: A new sequence called fluid and white matter suppression (FLAWS).Neuroimage Clin. 2018 Aug 11;20:388-397. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2018.08.010. eCollection 2018. Neuroimage Clin. 2018. PMID: 30128277 Free PMC article.
-
Usefulness of Intraoperative ultrasound for cortical dysplasia type I treatment - A single-center experience.Surg Neurol Int. 2023 Feb 24;14:62. doi: 10.25259/SNI_926_2022. eCollection 2023. Surg Neurol Int. 2023. PMID: 36895230 Free PMC article.
-
Epilepsy surgery for focal cortical dysplasia: Seizure and quality of life (QOLIE-89) outcomes.Neurol India. 2018 Nov-Dec;66(6):1655-1666. doi: 10.4103/0028-3886.246263. Neurol India. 2018. PMID: 30504559
-
Focal cortical dysplasia: etiology, epileptogenesis, classification, clinical presentation, imaging, and management.Childs Nerv Syst. 2020 Dec;36(12):2939-2947. doi: 10.1007/s00381-020-04851-9. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Childs Nerv Syst. 2020. PMID: 32766946 Review.
-
Seizure outcome following primary motor cortex-sparing resective surgery for perirolandic focal cortical dysplasia.Int J Surg. 2016 Dec;36(Pt B):466-476. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2015.10.036. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Int J Surg. 2016. PMID: 26542986 Review.
References
-
- Akeret K, Bellut D, Huppertz HJ, Ramantani G, König K, Serra C, et al. Ultrasonographic features of focal cortical dysplasia and their relevance for epilepsy surgery. Neurosurg Focus. 2018;45:E5. - PubMed
-
- Altieri R, Melcarne A, Junemann C, Zeppa P, Zenga F, Garbossa D, et al. Inferior Fronto-occipital fascicle anatomy in brain tumor surgeries: From anatomy lab to surgical theater. J Clin Neurosci. 2019;68:290–4. - PubMed
-
- Barba C, Barbati G, Di Giuda D, Fuggetta F, Papacci F, Meglio M, et al. Diagnostic yield and predictive value of provoked ictal SPECT in drug-resistant epilepsies. J Neurol. 2012;259:1613–22. - PubMed
-
- Bartolini L, Whitehead MT, Ho CY, Sepeta LN, Oluigbo CO, Havens K, et al. Temporal lobe epilepsy and focal cortical dysplasia in children: A tip to find the abnormality. Epilepsia. 2017;58:113–22. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
