Anti-urolithiatic, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of Erica arborea flowers and leaves hydromethanolic extracts: An ethnopharmacological study
- PMID: 37680977
- PMCID: PMC10480653
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2023.103785
Anti-urolithiatic, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of Erica arborea flowers and leaves hydromethanolic extracts: An ethnopharmacological study
Abstract
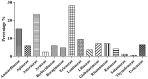
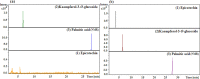
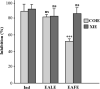
Erica arborea L. is a medicinal plant vastly used in therapeutic purposes in several parts of the world for antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and diuretic purposes, and in treating urinary infections and kidney stones. The current investigation aimed to evaluate the medicinal use of E. arborea in Algeria's Bejaia region, and to examine the anti-urolithiatic, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory (in vivo), analgesic, and toxicity effects of E. arborea hydromethanolic extracts from leaves (EALE) and flowers (EALE) to give a justification for its use in the traditional medicine. The in vitro anti-urolithiathic activity of E. arborea leaf and flower hydromethanolic extracts nucleation and aggregation of crystals were measured using spectrophotometric methods. The agar disk diffusion assay and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) determination were employed to estimate the antibacterial effect of EAME against three Gram-positive and three Gram-negative bacterial strains in vitro. In addition, the xylene and croton oil-induced ear edema methods in mice were used to examine the topical and oral anti-inflammatory potential of the extracts. Similarly, the analgesic effect of the extract was assessed via the acetic acid-induced abdominal constriction in mice, whereas the acute toxicity of EAME was conducted following OECD guidelines. An ethnobotanical survey was conducted among 171 informants with 212 questionnaire cards. Results indicated that 28.04 % of people in the studied region used E. arborea in traditional folk medicine. Additionally, results revealed the presence of epicatechin, palmitic acid, and kaempferol-3-O-glucoside in the plant extracts. Results also showed that EAME exhibits significant and dose-dependent anti-urolithiatic activity in nucleation and aggregation assays. Furthermore, results revealed that the extracts exhibit significant antibacterial activity. The E. arborea flower extract (EAFE) showed maximum antibacterial activity, especially against P. aeruginosa, E. coli, S. gallinarum, and B. cereus. In addition, a greater minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) in this extract was found at 1.60 mg/mL against M. luteus strain compared to the positive control. Moreover, the EAME caused a significant inhibition influence in the xylene and croton oil-induced edematous in mice. In contrast, the topical anti-inflammatory potential showed that extracts exhibit a considerable anti-edematogenic effect in both animal models. In the writhing reaction induced by the acetic acid model, the two extracts significantly reduced abdominal contractions. Finally, results of the toxicity assay showed that EAME is safe and no deaths or changes in mice behavior were observed even when doses as high as 5 g/kg DW were used. From the ethnopharmacological studies, our consequences endorse the benefit of E. arborea in folk medicine. Results of this investigation suggest that the leaf and flower extracts of E. arborea exhibit notable anti-urolithiatic, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antibacterial activities and are safe as a natural source of drugs with the above effects.
Keywords: Analgesic; Anti-inflammatory; Anti-urolithiatic; Antibacterial; Erica arborea; HPLC–MS.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-inflammatory, analgesic activity, and toxicity of Pituranthos scoparius stem extract: An ethnopharmacological study in rat and mouse models.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Aug 10;258:112936. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112936. Epub 2020 May 4. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32376367
-
In-vivo anti-inflammatory activity and safety assessment of the aqueous extract of Algerian Erica arborea L. (Ericaceae) aerial parts.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 May 10;271:113881. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113881. Epub 2021 Jan 27. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33508369
-
Analgesic, anti-inflammatory activity and metabolite profiling of the methanolic extract of Callicarpa arborea Roxb. leaves.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Jan 10;300:115757. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115757. Epub 2022 Sep 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36167233
-
Acute Oral Toxicity and Anti-inflammatory and Analgesic Effects of Aqueous and Methanolic Stem Bark Extracts of Piliostigma thonningii (Schumach.).Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Aug 6;2020:5651390. doi: 10.1155/2020/5651390. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32831869 Free PMC article.
-
Gmelina arborea- an indigenous timber species of India with high medicinal value: A review on its pharmacology, pharmacognosy and phytochemistry.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Mar 1;267:113593. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113593. Epub 2020 Nov 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33217516 Review.
Cited by
-
Mediterranean Basin Erica Species: Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Properties.Molecules. 2025 Jun 17;30(12):2616. doi: 10.3390/molecules30122616. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40572579 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abutaha, N., AL-Zharani, M., Alotaibi, A., Anne, M., Cordero, W., Bepari, A., Alarifi, S., 2021.In vitro and in vivo investigation of polypharmacology of propolis extract as anticancer, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and chemical properties. Chem.2(1), 864–874.
-
- Ahmed S., Hasan M.M., Mahmood Z.A. In vitro urolithiasis models: An evaluation of prophylactic management against kidney stones. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2016;5(3):28–35.
-
- Ahmed S., Hasan M.M., Alam Mahmood Z. Antiurolithiatic plants: Formulations used in different countries and cultures. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016;29(6):2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed S., Hasan M.M., Mahmood Z.A. Antiurolithiatic plants: Multidimensional pharmacology. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2016;5(2):04–24.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

