Obesity theranostics using nanoemulsions of probiotics and local herbs
- PMID: 37680978
- PMCID: PMC10480777
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2023.103790
Obesity theranostics using nanoemulsions of probiotics and local herbs
Abstract
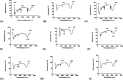
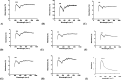
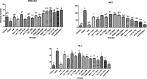
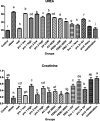
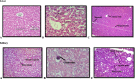
Obesity is a polygenic disorder which has become a global epidemic in recent years. Aim of the present study was to assess the theranostic potential of probiotics (Lactobacillus bulgaricus, Bifidobacterium) and local herbs (fenugreek seeds, aloe vera) on the body weight, biochemical (liver and kidney functions) and histology of some internal organs (liver, kidney, ovary, small intestine) in obese rats. In present study, nanoemulsions of probiotics and local herbs were formulated by high energy method and characterized by FTIR and UV analysis. One hundred and sixty (1 6 0) female wistar rats were divided into sixteen groups. A high-fat diet was given to induce obesity in them. Obese rats were treated with different doses of probiotics, local herbs and their combination. Weekly body weight was monitored. Rats were dissected after fifteen weeks; blood and organs were harvested for biochemical analysis and histology. Results demonstrated a protective effect of nanoemulsion of probiotics and local herbs on the central vein, glomerulus, villi and normal ovulatory function of obese rats. Rats treated with a combination of probiotics and local herbs (fenugreek seeds, aloe vera) exhibited improved levels of bilirubin (4 mg/dl to15 mg/dl), AST from (110 U/L to 18 U/L) and ALT from (52 U/L to 10U/L). Similar renoprotective effects were recorded on the overall renal function tests (RFT). A combination of probiotics and local herbs in post treatment rats improved urea (63 mg/dl to 22 mg/dl) and creatinine (0.2 mg/dl to 0.8 mg/dl) levels. It was therefore evident that a combination of probiotics and local herbs has the potential to reverse the effects of obesity on the biochemical parameters and histological architecture of liver, kidney, small intestine and ovary. The overall results indicated that probiotics have positive effects of their own, but when combined with local herbs, they produced highly effective results in obese rats and therefore can be used as a complementary option in obese individuals.
Keywords: High fat diet; Local herbs; Nanoemulsion; Obesity; Probiotics.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of immune response, microbiota, and blood markers after probiotic bacteria administration in obese mice induced by a high-fat diet.Nutrition. 2014 Nov-Dec;30(11-12):1423-32. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2014.03.025. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Nutrition. 2014. PMID: 25280423
-
Prophylactic effect of probiotics fortified with Aloe vera pulp nanoemulsion against ethanol-induced gastric ulcer.Toxicol Mech Methods. 2021 Nov;31(9):699-710. doi: 10.1080/15376516.2021.1958112. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2021. PMID: 34376109
-
Antiobesity and Uric Acid-Lowering Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum GKM3 in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obese Rats.J Am Coll Nutr. 2019 Sep-Oct;38(7):623-632. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2019.1571454. Epub 2019 Feb 22. J Am Coll Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30794474
-
Impact of bacterial probiotics on obesity, diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease related variables: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.BMJ Open. 2019 Mar 30;9(3):e017995. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-017995. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 30928918 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotics: How Effective Are They in the Fight against Obesity?Nutrients. 2019 Jan 24;11(2):258. doi: 10.3390/nu11020258. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30678355 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the neurovascular unit: Therapeutic potential of traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of stroke.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 20;10(19):e38200. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38200. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39386825 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akbari M., Rasouli H., Bahdor T. Physiological and pharmaceutical effect of fenugreek: A review. IOSR J. Pharm. 2012;2:49.
-
- Alatriste P.V.M., Arronte R.U., Espinosa C.O.G., Cuevas M.D.L.Á.E. Effect of probiotics on human blood urea levels in patients with chronic renal failure. Nutr. Hosp. 2014;29(3):582–590. - PubMed
-
- Anuradha C., Ravikumar P. Restoration on tissue antioxidants by fenugreek seeds (Trigonella Foenum Graecum) in alloxan-diabetic rats. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2001;45:408. - PubMed
-
- Badale A. Fenugreek seed and its active agent diosgenin treatment effects on different metabolic parameters in rats. Nal. Real. Acad. Nac. F. 2019;67(1):92–98.
-
- Bancroft, J.D., Gamble, M., 2008. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques. 6th ed. Elsevier Health Sciences. New York. U.S.A.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

