Effects of Climate Change on Soil Organic Matter C and H Isotope Composition in a Mediterranean Savannah (Dehesa): An Assessment Using Py-CSIA
- PMID: 37682017
- PMCID: PMC10515479
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.3c01816
Effects of Climate Change on Soil Organic Matter C and H Isotope Composition in a Mediterranean Savannah (Dehesa): An Assessment Using Py-CSIA
Abstract
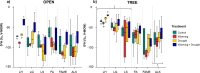
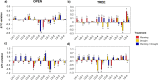
Dehesas are Mediterranean agro-sylvo-pastoral systems sensitive to climate change. Extreme climate conditions forecasted for Mediterranean areas may change soil C turnover, which is of relevance for soil biogeochemistry modeling. The effect of climate change on soil organic matter (SOM) is investigated in a field experiment mimicking environmental conditions of global change scenarios (soil temperature increase, +2-3 °C, W; rainfall exclusion, 30%, D; a combination of both, W+D). Pyrolysis-compound-specific isotope analysis (Py-CSIA) is used for C and H isotope characterization of SOM compounds and to forecast trends exerted by the induced climate shift. After 2.5 years, significant δ13C and δ2H isotopic enrichments were detected. Observed short- and mid-chain n-alkane δ13C shifts point to an increased microbial SOM reworking in the W treatment; a 2H enrichment of up to 40‰ of lignin methoxyphenols was found when combining W+D treatments under the tree canopy, probably related to H fractionation due to increased soil water evapotranspiration. Our findings indicate that the effect of the tree canopy drives SOM dynamics in dehesas and that, in the short term, foreseen climate change scenarios will exert changes in the SOM dynamics comprising the biogeochemical C and H cycles.
Keywords: Mediterranean soil; analytical pyrolysis; biomarkers; climate change; δ13C; δ2H.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Changes in soil organic matter molecular structure after five-years mimicking climate change scenarios in a Mediterranean savannah.Sci Total Environ. 2023 Jan 20;857(Pt 1):159288. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159288. Epub 2022 Oct 8. Sci Total Environ. 2023. PMID: 36220464
-
Impact of future scenarios of climate change on lignin dynamics in soil: A case study in a Mediterranean savannah.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Oct 10;946:174317. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.174317. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 38960189
-
Warming and increased precipitation indirectly affect the composition and turnover of labile-fraction soil organic matter by directly affecting vegetation and microorganisms.Sci Total Environ. 2020 Apr 20;714:136787. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136787. Epub 2020 Jan 18. Sci Total Environ. 2020. PMID: 31982765
-
Biogeochemistry of soil organic matter in agroecosystems & environmental implications.Sci Total Environ. 2019 Mar 25;658:1559-1573. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.243. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Sci Total Environ. 2019. PMID: 30678014 Review.
-
Molecular-level methods for monitoring soil organic matter responses to global climate change.J Environ Monit. 2011 May;13(5):1246-54. doi: 10.1039/c0em00752h. Epub 2011 Mar 17. J Environ Monit. 2011. PMID: 21416081 Review.
Cited by
-
Constraining activity and growth substrate of fungal decomposers via assimilation patterns of inorganic carbon and water into lipid biomarkers.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Apr 17;90(4):e0206523. doi: 10.1128/aem.02065-23. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38527003 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marschner B.; Brodowski S.; Dreves A.; Gleixner G.; Gude A.; Grootes P. M.; Hamer U.; Heim A.; Jandl G.; Ji R.; Kaiser K.; Kalbitz K.; Kramer C.; Leinweber P.; Rethemeyer J.; Schäffer A.; Schmidt M.; Schwark L.; Wiesenberg G. L. How relevant is recalcitrance for the stabilization of organic matter in soils?. J. Plant Nutr, Soil Sci. 2008, 171 (1), 91–110. 10.1002/jpln.200700049. - DOI
-
- Lal R. Managing soils and ecosystems for mitigating anthropogenic carbon emissions and advancing global food security. BioScience 2010, 60 (9), 708–721. 10.1525/bio.2010.60.9.8. - DOI
-
- Neupane A.; Lazicki P.; Mayes M. A.; Lee J.; Jagadamma S. The use of stable carbon isotopes to decipher global change effects on soil organic carbon: present status, limitations, and future prospects. Biogeochemistry 2022, 160 (3), 315–354. 10.1007/s10533-022-00963-3. - DOI
-
- Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Working Group I: contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC); Cambridge University Press: 2013; https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/wg1/.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

