Inhibition of β-lactamase function by de novo designed peptide
- PMID: 37682912
- PMCID: PMC10490870
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290845
Inhibition of β-lactamase function by de novo designed peptide
Abstract
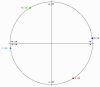
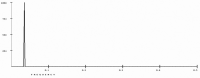
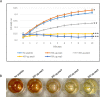
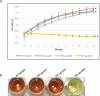
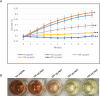
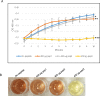
Antimicrobial resistance is a great public health concern that is now described as a "silent pandemic". The global burden of antimicrobial resistance requires new antibacterial treatments, especially for the most challenging multidrug-resistant bacteria. There are various mechanisms by which bacteria develop antimicrobial resistance including expression of β-lactamase enzymes, overexpression of efflux pumps, reduced cell permeability through downregulation of porins required for β-lactam entry, or modifications in penicillin-binding proteins. Inactivation of the β-lactam antibiotics by β-lactamase enzymes is the most common mechanism of bacterial resistance to these agents. Although several effective small-molecule inhibitors of β-lactamases such as clavulanic acid and avibactam are clinically available, they act only on selected class A, C, and some class D enzymes. Currently, none of the clinically approved inhibitors can effectively inhibit Class B metallo-β-lactamases. Additionally, there is increased resistance to these inhibitors reported in several bacteria. The objective of this study is to use the Resonant Recognition Model (RRM), as a novel strategy to inhibit/modulate specific antimicrobial resistance targets. The RRM is a bio-physical approach that analyzes the distribution of energies of free electrons and posits that there is a significant correlation between the spectra of this energy distribution and related protein biological activity. In this study, we have used the RRM concept to evaluate the structure-function properties of a group of 22 β-lactamase proteins and designed 30-mer peptides with the desired RRM spectral periodicities (frequencies) to function as β-lactamase inhibitors. In contrast to the controls, our results indicate 100% inhibition of the class A β-lactamases from Escherichia coli and Enterobacter cloacae. Taken together, the RRM model can likely be utilized as a promising approach to design β-lactamase inhibitors for any specific class. This may open a new direction to combat antimicrobial resistance.
Copyright: © 2023 Mishra et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clavulanic acid inactivation of SHV-1 and the inhibitor-resistant S130G SHV-1 beta-lactamase. Insights into the mechanism of inhibition.J Biol Chem. 2005 Oct 21;280(42):35528-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M501251200. Epub 2005 Jun 29. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15987690
-
Avibactam and inhibitor-resistant SHV β-lactamases.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Jul;59(7):3700-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04405-14. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25691639 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Peptide-based Metallo-β-lactamase Inhibitors as a New Strategy to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance: A Mini-review.Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(44):3538-3545. doi: 10.2174/1381612828666220929154255. Curr Pharm Des. 2022. PMID: 36177630 Review.
-
Exploring the potential of boronic acids as inhibitors of OXA-24/40 β-lactamase.Protein Sci. 2017 Mar;26(3):515-526. doi: 10.1002/pro.3100. Epub 2017 Feb 23. Protein Sci. 2017. PMID: 27997706 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-lactamase inhibitors: the story so far.Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(28):3740-65. doi: 10.2174/092986709789104957. Curr Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19747143 Review.
Cited by
-
Breakthrough Advances in Beta-Lactamase Inhibitors: New Synthesized Compounds and Mechanisms of Action Against Drug-Resistant Bacteria.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Feb 3;18(2):206. doi: 10.3390/ph18020206. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different SARS-CoV-2 variants inhibited by RRM designed peptide.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 22;20(7):e0327582. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327582. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40694559 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fleming A. On the antibacterial action of cultures of a penicillium, with special reference to their use in the isolation of B. influenzae. British journal of experimental pathology. 1929;10(3):226.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

