Identification of ROCK1 as a novel biomarker for postmenopausal osteoporosis and pan-cancer analysis
- PMID: 37683138
- PMCID: PMC10522383
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205004
Identification of ROCK1 as a novel biomarker for postmenopausal osteoporosis and pan-cancer analysis
Abstract
Background: Postmenopausal osteoporosis (PMOP) is a prevalent bone disorder with significant global impact. The elevated risk of osteoporotic fracture in elderly women poses a substantial burden on individuals and society. Unfortunately, the current lack of dependable diagnostic markers and precise therapeutic targets for PMOP remains a major challenge.
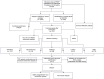
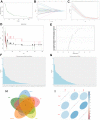
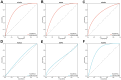
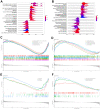
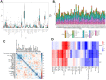
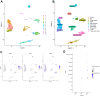
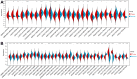
Methods: PMOP-related datasets GSE7429, GSE56814, GSE56815, and GSE147287, were downloaded from the GEO database. The DEGs were identified by "limma" packages. WGCNA and Machine Learning were used to choose key module genes highly related to PMOP. GSEA, DO, GO, and KEGG enrichment analysis was performed on all DEGs and the selected key hub genes. The PPI network was constructed through the GeneMANIA database. ROC curves and AUC values validated the diagnostic values of the hub genes in both training and validation datasets. xCell immune infiltration and single-cell analysis identified the hub genes' function on immune reaction in PMOP. Pan-cancer analysis revealed the role of the hub genes in cancers.
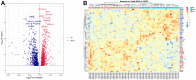
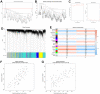
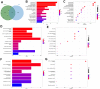
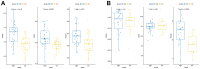
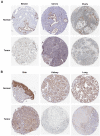
Results: A total of 1278 DEGs were identified between PMOP patients and the healthy controls. The purple module and cyan module were selected as the key modules and 112 common genes were selected after combining the DEGs and module genes. Five Machine Learning algorithms screened three hub genes (KCNJ2, HIPK1, and ROCK1), and a PPI network was constructed for the hub genes. ROC curves validate the diagnostic values of ROCK1 in both the training (AUC = 0.73) and validation datasets of PMOP (AUC = 0.81). GSEA was performed for the low-ROCK1 patients, and the top enriched field included protein binding and immune reaction. DCs and NKT cells were highly expressed in PMOP. Pan-cancer analysis showed a correlation between low ROCK1 expression and SKCM as well as renal tumors (KIRP, KICH, and KIRC).
Conclusions: ROCK1 was significantly associated with the pathogenesis and immune infiltration of PMOP, and influenced cancer development, progression, and prognosis, which provided a potential therapy target for PMOP and tumors. However, further laboratory and clinical evidence is required before the clinical application of ROCK1 as a therapeutic target.
Keywords: ROCK1; immune infiltration; machined Learning; pan-cancer; postmenopausal osteoporosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- International Osteoporosis Foundation. About Osteoporosis. 2023. https://www.osteoporosis.foundation/patients/about-osteoporosis.
-
- International Osteoporosis Foundation. Diagnosis of Osteoporosis. 2023. https://www.osteoporosis.foundation/patients/diagnosis.
-
- Estrada K, Styrkarsdottir U, Evangelou E, Hsu YH, Duncan EL, Ntzani EE, Oei L, Albagha OM, Amin N, Kemp JP, Koller DL, Li G, Liu CT, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies 56 bone mineral density loci and reveals 14 loci associated with risk of fracture. Nat Genet. 2012; 44:491–501. 10.1038/ng.2249 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Trajanoska K, Morris JA, Oei L, Zheng HF, Evans DM, Kiel DP, Ohlsson C, Richards JB, Rivadeneira F, and GEFOS/GENOMOS consortium and the 23andMe research team. Assessment of the genetic and clinical determinants of fracture risk: genome wide association and mendelian randomisation study. BMJ. 2018; 362:k3225. 10.1136/bmj.k3225 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

