Evaluating the Performance of the Astral Mass Analyzer for Quantitative Proteomics Using Data-Independent Acquisition
- PMID: 37683181
- PMCID: PMC10563156
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.3c00357
Evaluating the Performance of the Astral Mass Analyzer for Quantitative Proteomics Using Data-Independent Acquisition
Abstract
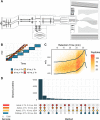
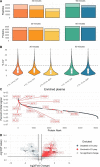
We evaluate the quantitative performance of the newly released Asymmetric Track Lossless (Astral) analyzer. Using data-independent acquisition, the Thermo Scientific Orbitrap Astral mass spectrometer quantifies 5 times more peptides per unit time than state-of-the-art Thermo Scientific Orbitrap mass spectrometers, which have long been the gold standard for high-resolution quantitative proteomics. Our results demonstrate that the Orbitrap Astral mass spectrometer can produce high-quality quantitative measurements across a wide dynamic range. We also use a newly developed extracellular vesicle enrichment protocol to reach new depths of coverage in the plasma proteome, quantifying over 5000 plasma proteins in a 60 min gradient with the Orbitrap Astral mass spectrometer.
Keywords: data-independent acquisition; high-resolution mass spectrometry; plasma; quantitative proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): The MacCoss Lab at the University of Washington has a sponsored research agreement with Thermo Fisher Scientific, the manufacturer of the instrumentation used in this research. However, analytical techniques were selected and performed independent of Thermo Fisher Scientific. M.J.M. is a paid consultant for Thermo Fisher Scientific. E.D., T.N.A., A.C.P., E.D., J.P., A.P., P.M.R., M.W.S., H.I.S., C.H., A.A.M., D.H., and V.Z. are employees of Thermo Fisher Scientific, the manufacturer of the instrumentation used in this research.
Figures


Update of
-
Evaluating the Performance of the Astral Mass Analyzer for Quantitative Proteomics Using Data Independent Acquisition.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 7:2023.06.03.543570. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.03.543570. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Proteome Res. 2023 Oct 6;22(10):3290-3300. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.3c00357. PMID: 37398334 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Brunner A.-D.; Thielert M.; Vasilopoulou C. G.; Ammar C.; Coscia F.; Mund A.; Hoerning O. B.; Bache N.; Apalategui A.; Lubeck M.; Richter S.; Fischer D. S.; Raether O.; Park M. A.; Meier F.; Theis F. J.; Mann M. Ultra-High Sensitivity Mass Spectrometry Quantifies Single-Cell Proteome Changes upon Perturbation. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2022, 18, e1079810.15252/msb.202110798. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

