Biomarker-based risk prediction for the onset of neuroinflammation in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy
- PMID: 37683329
- PMCID: PMC10497986
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104781
Biomarker-based risk prediction for the onset of neuroinflammation in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy
Abstract
Background: X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) is highly variable, ranging from slowly progressive adrenomyeloneuropathy to severe brain demyelination and inflammation (cerebral ALD, CALD) affecting males with childhood peak onset. Risk models integrating blood-based biomarkers to indicate CALD onset, enabling timely interventions, are lacking. Therefore, we evaluated the prognostic value of blood biomarkers in addition to current neuroimaging predictors for early detection of CALD.
Methods: We measured blood biomarkers in a retrospective, male CALD risk-assessment cohort consisting of 134 X-ALD patients and 66 controls and in a phenotype-blinded validation set (25 X-ALD boys, 4-13 years) using Simoa®and Luminex® technologies.
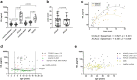
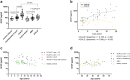
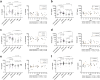
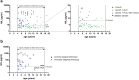
Findings: Among 25 biomarkers indicating axonal damage, astrocye/microglia activation, or immune-cell recruitment, neurofilament light chain (NfL) had the highest prognostic value for early indication of childhood/adolescent CALD. A plasma NfL cut-off level of 8.33 pg/mL, determined in the assessment cohort, correctly discriminated CALD with an accuracy of 96% [95% CI: 80-100] in the validation group. Multivariable logistic regression models revealed that combining NfL with GFAP or cytokines/chemokines (IL-15, IL-12p40, CXCL8, CCL11, CCL22, and IL-4) that were significantly elevated in CALD vs healthy controls had no additional benefit for detecting neuroinflammation. Some cytokines/chemokines were elevated only in childhood/adolescent CALD and already upregulated in asymptomatic X-ALD children (IL-15, IL-12p40, and CCL7). In adults, NfL levels distinguished CALD but were lower than in childhood/adolescent CALD patients with similar (MRI) lesion severity. Blood GFAP did not differentiate CALD from non-inflammatory X-ALD.
Interpretation: Biomarker-based risk prediction with a plasma NfL cut-off value of 8.33 pg/mL, determined by ROC analysis, indicates CALD onset with high sensitivity and specificity in childhood X-ALD patients. A specific pro-inflammatory cytokine/chemokine profile in asymptomatic X-ALD boys may indicate a primed, immanent inflammatory state aligning with peak onset of CALD. Age-related differences in biomarker levels in adult vs childhood CALD patients warrants caution in predicting onset and progression of CALD in adults. Further evaluations are needed to assess clinical utility of the NfL cut-off for risk prognosis of CALD onset.
Funding: Austrian Science Fund, European Leukodystrophy Association.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cytokines; GFAP; Neurodegeneration; Neurofilament light chain; X-ALD.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests MP received support from Amicus, Merck, Novartis and Sanofi-Genzyme; BZ received support from ACTRIMS 2022 and 2023 endMS SPRINT; JG received support from Quanterix; HAY was supported by an emerging investigator grant from ALD connect; CGB received grants from the German Research Foundation and the Ministry for Science and Culture of Lower Saxony; ME received support from Minoryx and is member of the advisory board of Minoryx, Poxel and SwanBio Therapeutics; FE is holding a license for “Intrathecal delivery of nucleic acid sequences encoding ABCD1 for treatment of Adrenomyeloneuropathy” (NO. 29539-021PCT), received consulting fees from SwanBio Therapeutics and UpToDate, is founder of SwanBio Therapeutics, ALD Connect and organizer of trial sites for ASPA, Bluebird Bio Therapeutics, Ionis Pharmaceuticals and Sanofi; AP received consulting fees from Swanbio Therapeutics and Sanofi and is member of the Advisory Board of Bluebird Bio Therapeutics and MedDay Therapeutics. JSK is member of the advisory board for Krabbe Disease of PassageBio. MCR received a grant from Novartis. EM has received funding from the National Institutes of Health (K23NS118044). All remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Mosser J., Douar A.M., Sarde C.O., et al. Putative X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy gene shares unexpected homology with ABC transporters. Nature. 1993;361(6414):726–730. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

