De novo TRPM3 missense variant associated with neurodevelopmental delay and manifestations of cerebral palsy
- PMID: 37684057
- PMCID: PMC10815282
- DOI: 10.1101/mcs.a006293
De novo TRPM3 missense variant associated with neurodevelopmental delay and manifestations of cerebral palsy
Abstract
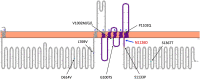
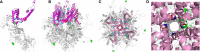
We identified a de novo heterozygous transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M (melastatin) member 3 (TRPM3) missense variant, p.(Asn1126Asp), in a patient with developmental delay and manifestations of cerebral palsy (CP) using phenotype-driven prioritization analysis of whole-genome sequencing data with Exomiser. The variant is localized in the functionally important ion transport domain of the TRPM3 protein and predicted to impact the protein structure. Our report adds TRPM3 to the list of Mendelian disease-associated genes that can be associated with CP and provides further evidence for the pathogenicity of the variant p.(Asn1126Asp).
Keywords: absent speech; bilateral convulsive seizures; bilateral talipes equinovarus; broad forehead; deeply set eye; intellectual disability, moderate; language impairment; moderate global developmental delay; thoracic scoliosis; torticollis.
© 2023 Sundaramurthi et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
References
-
- Burglen L, Van Hoeymissen E, Qebibo L, Barth M, Belnap N, Boschann F, Depienne C, De Clercq K, Douglas AGL, Fitzgerald MP, et al. 2023. Gain-of-function variants in the ion channel gene TRPM3 underlie a spectrum of neurodevelopmental disorders. eLife 12: e81032. 10.7554/eLife.81032 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Sainte Agathe J-M, Van-Gils J, Lasseaux E, Arveiler B, Lacombe D, Pfirrmann C, Raclet V, Gaston L, Plaisant C, Aupy J, et al. 2020. Confirmation and expansion of the phenotype associated with the recurrent p.Val837Met variant in TRPM3. Eur J Med Genet 63: 103942. 10.1016/j.ejmg.2020.103942 - DOI - PubMed
