Production of perillic acid from orange essential oil by Yarrowia lipolytica using a top-aerated bioreactor
- PMID: 37684539
- PMCID: PMC10689591
- DOI: 10.1007/s42770-023-01108-w
Production of perillic acid from orange essential oil by Yarrowia lipolytica using a top-aerated bioreactor
Abstract
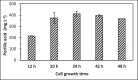
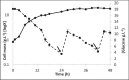
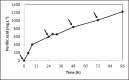
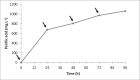
R-(+)-Perillic acid, a promising anticancer and immunomodulatory agent, is the major product from the biotransformation of R-(+)-limonene-rich orange essential oil by the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Due to the abundance and low cost of orange essential oil, which is a byproduct of the citrus industry, we attempted to improve the biotransformation process by optimizing yeast cell mass production. Then, the whole process was transposed and adapted to a 2-L instrumented bioreactor. Cell mass production was optimized in shaker flasks using a statistical experimental design. The optimized medium (g·L-1: 22.9 glucose, 7.7 peptone, 4.1 yeast extract and 1.0 malt extract) resulted in a 13.0 g·L-1 final cell concentration and 0.18 g cell·L-1·h-1 productivity. A further increase to 18.0 g·L-1 was achieved in a 2-L bioreactor upon fed-batch culture. High-purity limonene bioconversion was performed in the same bioreactor utilizing top aeration to diminish terpene volatilization; as a result, 839.6 mg·L-1 perillic acid accumulated after 48 h. Under the same conditions, industrial orange essential oil afforded 806.4 mg·L-1 perillic acid. The yeast growth medium optimization resulted in a twofold increase in biomass accumulation and a reduction in growth medium nitrogen sources, which lowered the catalytic biomass production cost. Compared with conventional bottom aeration, the bioreactor top aeration strategy resulted in higher bioconversion rates. The conditions developed for high-purity limonene bioconversion were successfully applied to low-cost orange essential oil, showing the robustness of Y. lipolytica yeast.
Keywords: Biotransformation; Limonene; Orange essential oil; Perillic acid; Top-aerated bioreactor; Yarrowia lipolytica.
© 2023. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Sociedade Brasileira de Microbiologia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sun J. D-Limonene: safety and clinical applications. Altern Med Rev. 2007;12:259–264. - PubMed
-
- Ariazi EA, Satomi Y, Ellis MJ, Haag JD, Shi W, Sattler CA, Gould MN. Activation of the transforming growth factor beta signaling pathway and induction of cytostasis and apoptosis in mammary carcinomas treated with the anticancer agent perillyl alcohol. Cancer Res. 1999;59:1917–1928. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PROEP/FAR/CNPq 407841/2017-2/Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico
- 307766/2014/4/Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico
- PIBIC/CNPq/FIOCRUZ 2014-2016/Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico
- E-26/101.210/2013/Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro
- E-26/110.856/2013/Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

