Effect of education regarding treatment guidelines for schizophrenia and depression on the treatment behavior of psychiatrists: A multicenter study
- PMID: 37684711
- PMCID: PMC11488608
- DOI: 10.1111/pcn.13578
Effect of education regarding treatment guidelines for schizophrenia and depression on the treatment behavior of psychiatrists: A multicenter study
Abstract
Aim: This study aims to examine the real-world effectiveness of education regarding clinical guidelines for psychiatric disorders using 'the Effectiveness of guidelines for dissemination and education in psychiatric treatment (EGUIDE)' project.
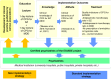
Methods: The EGUIDE project is a nationwide prospective implementation study of two clinical practice guidelines, i.e., the Guideline for Pharmacological Therapy of Schizophrenia and the Treatment Guidelines for Major Depressive Disorders, in Japan. Between 2016 and 2019, 782 psychiatrists belonging to 176 hospitals with psychiatric wards participated in the project and attended lectures on clinical practice guidelines. The proportions of guideline-recommended treatments in 7405 patients with schizophrenia and 3794 patients with major depressive disorder at participating hospitals were compared between patients under the care of psychiatrists participating in the project and those not participating in the project. Clinical and prescribing data on the patients discharged from April to September each year from participating hospitals of the project were also analyzed.
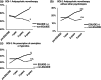
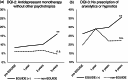
Results: The proportions of three quality indicators (antipsychotic monotherapy regardless of whether other psychotropics medication, antipsychotic monotherapy without other psychotropics and no prescription of anxiolytics or hypnotics) for schizophrenia were higher among participating psychiatrists than among nonparticipating psychiatrists. As similar results were obtained in major depressive disorder, the effectiveness of the project for the dissemination of guideline-recommended treatment has been replicated.
Conclusion: This strategy of providing education regarding the clinical guidelines for psychiatric disorders was effective in improving the treatment-related behavior of psychiatrists. The use of this education-based strategy might contribute to resolving the mental health treatment gap.
Keywords: clinical practice guideline; dissemination; education; major depressive disorder; schizophrenia.
© 2023 The Authors. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Society of Psychiatry and Neurology.
Figures
References
-
- Djulbegovic B, Guyatt GH. Progress in evidence‐based medicine: A quarter century on. Lancet 2017; 390: 415–423. - PubMed
-
- Keepers GA, Fochtmann LJ, Anzia JM et al. The American Psychiatric Association practice guideline for the treatment of patients with schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2020; 177: 868–872. - PubMed
-
- Kuipers E, Yesufu‐Udechuku A, Taylor C, Kendall T. Management of psychosis and schizophrenia in adults: Summary of updated NICE guidance. BMJ 2014; 348: g1173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- JP16dk0307060/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- JP19dk0307083/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- JP22dk0307112/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- JHP2022-J-02/Japan Health Research Promotion Bureau Project Fund
- JP21K17261/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research
- 19GC1012/Health and Labor Sciences Research Grants from The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
- H29-Seishin-Ippan-001/Health and Labor Sciences Research Grants from The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
- the Japanese Society of Clinical Neuropsychopharmacology
- the Japanese Society of Mood Disorders
- the Japanese Society of Neuropsychopharmacology
- the Japanese Society of Psychiatry and Neurology
- 2019-(1)-4/the National Center Consortium in Implementation Science for Health Equity (N-EQUITY) from the Japan Health Research Promotion Bureau (JH) Research Fund
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

