Antibacterial Effects of Ramulus mori Oligosaccharides against Streptococcus mutans
- PMID: 37685114
- PMCID: PMC10486356
- DOI: 10.3390/foods12173182
Antibacterial Effects of Ramulus mori Oligosaccharides against Streptococcus mutans
Abstract
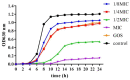
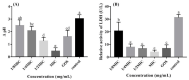
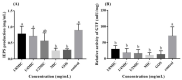
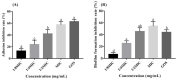
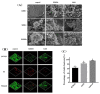
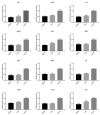
Ramulus mori has been widely used in traditional Chinese medicine because of its physiological activities, including antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant activities. Antimicrobial properties of Ramulus mori extract have been well described. However, no information is available regarding on Ramulus mori oligosaccharides (RMOS). The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of RMOS on the growth and virulence properties of the cariogenic bacterium Streptococcus mutans. The effects of RMOS on the biofilm structure and virulence gene expression of S. mutans were also evaluated, and the results were compared with the effects of commercial prebiotic galactooligosaccharides. RMOS were found to have an antibacterial effect against S. mutans, resulting in significant reductions in acid production, lactate dehydrogenase activity, adhesion, insoluble extracellular polysaccharide production, glucosyltransferase activity, and biofilm formation in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, the biofilm structure was visibly damaged. A quantitative real-time PCR assay revealed downregulation of virulence gene-regulated acid production, polysaccharide production, adhesion, biofilm formation, and quorum sensing. These findings suggest that RMOS may be a promising natural product for the prevention of dental caries.
Keywords: Ramulus mori oligosaccharides; Streptococcus mutans; anti-caries; antibacterial; biofilm.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibacterial mechanism of areca nut essential oils against Streptococcus mutans by targeting the biofilm and the cell membrane.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Aug 28;13:1140689. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1140689. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37701779 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Rubusoside, a Natural Sucrose Substitute, on Streptococcus mutans Biofilm Cariogenic Potential and Virulence Gene Expression In Vitro.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020 Aug 3;86(16):e01012-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01012-20. Print 2020 Aug 3. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32503907 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Antimicrobial Peptide GH12 on the Cariogenic Properties and Composition of a Cariogenic Multispecies Biofilm.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Nov 30;84(24):e01423-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01423-18. Print 2018 Dec 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30341079 Free PMC article.
-
Dlt operon regulates physiological function and cariogenic virulence in Streptococcus mutans.Future Microbiol. 2023 Mar;18:225-233. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2022-0165. Epub 2023 Apr 25. Future Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37097048 Review.
-
Quorum sensing and biofilm formation by Streptococcus mutans.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;631:178-88. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-78885-2_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18792689 Review.
References
-
- Rossoni R.D., dos Santos Velloso M., de Barros P.P., de Alvarenga J.A., Dos Santos J.D., dos Santos Prado A.C.C., de Camargo Ribeiro F., Anbinder A.L., Junqueira J.C. Inhibitory effect of probiotic Lactobacillus supernatants from the oral cavity on Streptococcus mutans biofilms. Microb. Pathog. 2018;123:361–367. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.07.032. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- AB21196040/Science and Technology Plan Project of Guangxi Province
- The Special Financial Fund of Foshan in 2023-Cooperation project for high-level agricultural science and technology demonstration city construction in Guangdong Province
- No. 202119TD/Agricultural competitive industry discipline team building project of Guangdong Academy of Agricultural Sciences
- 2023KJ124/Guangdong Modern Agricultural Industry Technology System Innovation Team
- China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

