A Biopsychosocial Model Predicting Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 37685782
- PMCID: PMC10489059
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12175715
A Biopsychosocial Model Predicting Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
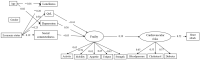
Myocardial infarction is one of the main causes of death, and cardiovascular risk factors (CVRFs) are always considered when studying it. However, although it is known that other social and psychological variables, and especially frailty, can increase the risk of infarction, their simultaneous effect has not been extensively studied. This study is based on data from the SHARE project (latest wave, Wave 8), with a representative sample of 46,498 participants aged 50 or older (M = 70.40, SD = 9.33), of whom 57.4% were females. Statistical analyses included a full structural equation model that predicts 27% of infarction occurrence and evidences the significant effect of well-being, depression, and social connectedness on frailty. Frailty, in turn, explains 15.5% of the variability of CVRFs. This work supports the need to study these physical, social, and mental health factors together to intervene on frailty and, in turn, improve cardiovascular outcomes.
Keywords: SHARE survey; aging; biopsychosocial approach; cardiovascular disease; coronary artery disease; frailty.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Roth G.A., Mensah G.A., Johnson C.O., Addolorato G., Ammirati E., Baddour L.M. GBD-NHLBI-JACC Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases Writing Group. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020;76:2982–3021. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Roth G.A., Abate D., Abate K.H., Abay S.M., Abbafati C., Abbasi N., Abbastabar H., Abd-Allah F., Abdela J., Abdelalim A., et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1736–1788. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32203-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources