Using Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins as Potential Biomarkers to Discriminate between Parkinson's Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies: Exploration of a Novel Technique
- PMID: 37686075
- PMCID: PMC10487513
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241713267
Using Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins as Potential Biomarkers to Discriminate between Parkinson's Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies: Exploration of a Novel Technique
Abstract
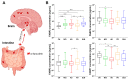
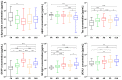
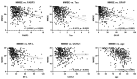
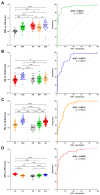
An increase in the global aging population is leading to an increase in age-related conditions such as dementia and movement disorders, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB). The accurate prediction of risk factors associated with these disorders is crucial for early diagnosis and prevention. Biomarkers play a significant role in diagnosing and monitoring diseases. In neurodegenerative disorders like α-synucleinopathies, specific biomarkers can indicate the presence and progression of disease. We previously demonstrated the pathogenic impact of fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs) in α-synucleinopathies. Therefore, this study investigated FABPs as potential biomarkers for Lewy body diseases. Plasma FABP levels were measured in patients with AD, PD, DLB, and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and healthy controls. Plasma FABP3 was increased in all groups, while the levels of FABP5 and FABP7 tended to decrease in the AD group. Additionally, FABP2 levels were elevated in PD. A correlation analysis showed that higher FABP3 levels were associated with decreased cognitive function. The plasma concentrations of Tau, GFAP, NF-L, and UCHL1 correlated with cognitive decline. A scoring method was applied to discriminate between diseases, demonstrating high accuracy in distinguishing MCI vs. CN, AD vs. DLB, PD vs. DLB, and AD vs. PD. The study suggests that FABPs could serve as potential biomarkers for Lewy body diseases and aid in early disease detection and differentiation.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; biomarkers; dementia; dementia with Lewy bodies; diagnosis; discrimination technique; fatty acid-binding proteins; α-synucleinopathies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential role of CSF fatty acid binding protein 3, α-synuclein, and Alzheimer's disease core biomarkers in Lewy body disorders and Alzheimer's dementia.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2017 Jul 28;9(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s13195-017-0276-4. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28750675 Free PMC article.
-
Parkinson's and Lewy body dementia CSF biomarkers.Clin Chim Acta. 2019 Aug;495:318-325. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.04.078. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Clin Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31051162 Review.
-
Salivary biomarkers for the molecular diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies.J Alzheimers Dis. 2025 Mar;104(2):452-462. doi: 10.1177/13872877251317720. Epub 2025 Mar 14. J Alzheimers Dis. 2025. PMID: 40084669
-
The potential of erythrocyte α-synuclein to differentiate dementia with Lewy bodies from Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases.J Biochem. 2025 May 30;177(6):415-424. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvaf017. J Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40235217
-
Dementia with Lewy bodies.Semin Clin Neuropsychiatry. 2003 Jan;8(1):46-57. doi: 10.1053/scnp.2003.50006. Semin Clin Neuropsychiatry. 2003. PMID: 12567332 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenic Impact of Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins in Parkinson's Disease-Potential Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 1;24(23):17037. doi: 10.3390/ijms242317037. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differences in Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid Between Parkinson's Disease and Related Diseases.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Dec 27;45(1):9. doi: 10.1007/s10571-024-01523-z. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39729132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative quantitation of liver-type fatty acid-binding protein localizations in liver injury and non-pathological liver tissue in dogs.Vet World. 2024 Feb;17(2):313-318. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2024.313-318. Epub 2024 Feb 7. Vet World. 2024. PMID: 38595649 Free PMC article.
-
Associations among blood biomarkers, clinical subtypes, and prognosis in Parkinson's disease.Clin Park Relat Disord. 2025 Mar 11;12:100313. doi: 10.1016/j.prdoa.2025.100313. eCollection 2025. Clin Park Relat Disord. 2025. PMID: 40161513 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fukui N., Yamamoto H., Miyabe M., Aoyama Y., Hongo K., Mizobata T., Kawahata I., Yabuki Y., Shinoda Y., Fukunaga K., et al. An alpha-synuclein decoy peptide prevents cytotoxic alpha-synuclein aggregation caused by fatty acid binding protein 3. J. Biol. Chem. 2021;296:100663. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100663. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

