Transcriptional Regulators of Plant Adaptation to Heat Stress
- PMID: 37686100
- PMCID: PMC10487819
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241713297
Transcriptional Regulators of Plant Adaptation to Heat Stress
Abstract
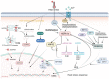
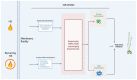
Heat stress (HS) is becoming an increasingly large problem for food security as global warming progresses. As sessile species, plants have evolved different mechanisms to cope with the disruption of cellular homeostasis, which can impede plant growth and development. Here, we summarize the mechanisms underlying transcriptional regulation mediated by transcription factors, epigenetic regulators, and regulatory RNAs in response to HS. Additionally, cellular activities for adaptation to HS are discussed, including maintenance of protein homeostasis through protein quality control machinery, and autophagy, as well as the regulation of ROS homeostasis via a ROS-scavenging system. Plant cells harmoniously regulate their activities to adapt to unfavorable environments. Lastly, we will discuss perspectives on future studies for improving urban agriculture by increasing crop resilience to HS.
Keywords: ROS homeostasis; epigenetics; heat stress; histone modification; protein homeostasis; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Corlett R.T. Climate change in the tropics: The end of the world as we know it? Biol. Conserv. 2012;151:22–25. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2011.11.027. - DOI
-
- Tao F.L., Zhang S.A., Zhu Z. Changes in rice disasters across China in recent decades and the meteorological and agronomic causes. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2012;13:743–759. doi: 10.1007/s10113-012-0357-7. - DOI
-
- Miller S., Chua K., Coggins J., Mohtadi H. Heat Waves, Climate Change, and Economic Output. J. Eur. Econ. Assoc. 2021;19:2658–2694. doi: 10.1093/jeea/jvab009. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

