Significance of the cGAS-STING Pathway in Health and Disease
- PMID: 37686127
- PMCID: PMC10487967
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241713316
Significance of the cGAS-STING Pathway in Health and Disease
Abstract
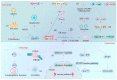
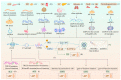
The cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)-stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway plays a significant role in health and disease. In this pathway, cGAS, one of the major cytosolic DNA sensors in mammalian cells, regulates innate immunity and the STING-dependent production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including type-I interferon. Moreover, the cGAS-STING pathway is integral to other cellular processes, such as cell death, cell senescence, and autophagy. Activation of the cGAS-STING pathway by "self" DNA is also attributed to various infectious diseases and autoimmune or inflammatory conditions. In addition, the cGAS-STING pathway activation functions as a link between innate and adaptive immunity, leading to the inhibition or facilitation of tumorigenesis; therefore, research targeting this pathway can provide novel clues for clinical applications to treat infectious, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases and even cancer. In this review, we focus on the cGAS-STING pathway and its corresponding cellular and molecular mechanisms in health and disease.
Keywords: anti-pathogen immunity; autoimmune disorder; cGAS–STING pathway; cancer; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

