Upregulation of Orai Channels Contributes to Aging-Related Vascular Alterations in Rat Coronary Arteries
- PMID: 37686206
- PMCID: PMC10487684
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241713402
Upregulation of Orai Channels Contributes to Aging-Related Vascular Alterations in Rat Coronary Arteries
Abstract
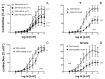
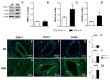
Vascular territories display heterogeneous sensitivity to the impacts of aging. The relevance of the STIM/Orai system to vascular function depends on the vascular bed. We aimed to evaluate the contribution of the STIM/Orai system to aging-related vascular dysfunction in rat coronary circulation. Vascular function was evaluated according to myography in coronary arteries from young (three-month-old) and older (twenty-month-old) rats. The effects of aging and STIM/Orai inhibition on the contraction and relaxation of the coronary arteries and on the protein expression of STIM-1, Orai1, and Orai3 in these vessels were determined. Aging-related hypercontractility to serotonin and endothelin-1 in arteries from male rats was reversed by STIM/Orai inhibition with YM-58483 or by specifically blocking the Orai1 channel with Synta66. The inhibitory effects of Synta66 on coronary vasoconstriction were also observed in older female rats. YM-58483 relaxed serotonin- but not KCl-contracted arteries from males. STIM/Orai inhibition improved defective endothelial vasodilations in aged arteries, even in the presence of NO synthase and cyclooxygenase inhibitors, but not in KCl-contracted segments. YM-58483 significantly enhanced relaxations to calcium-activated potassium channel stimulation in aged vessels. Increased protein expression of Orai1 and Orai3 was detected in arterial homogenates and sections from older rats. Upregulation of the Orai channel contributes to aging-related coronary dysfunction, revealing a potential target in reducing CVD risk.
Keywords: Orai channel; arterial hypercontractility; coronary artery; endothelial function; vascular aging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ageing-induced hypercontractility is related to functional enhancement of STIM/Orai and upregulation of Orai 3 in rat and human penile tissue.Mech Ageing Dev. 2021 Dec;200:111590. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2021.111590. Epub 2021 Oct 23. Mech Ageing Dev. 2021. PMID: 34699858
-
Functional Role of STIM-1 and Orai1 in Human Microvascular Aging.Cells. 2022 Nov 18;11(22):3675. doi: 10.3390/cells11223675. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36429103 Free PMC article.
-
STIM/Orai Inhibition as a Strategy for Alleviating Diabetic Erectile Dysfunction Through Modulation of Rat and Human Penile Tissue Contractility and in vivo Potentiation of Erectile Responses.J Sex Med. 2022 Dec;19(12):1733-1749. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2022.08.200. Epub 2022 Oct 1. J Sex Med. 2022. PMID: 36195535
-
STIM and Orai Mediated Regulation of Calcium Signaling in Age-Related Diseases.Front Aging. 2022 Apr 19;3:876785. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2022.876785. eCollection 2022. Front Aging. 2022. PMID: 35821821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox modulation of STIM-ORAI signaling.Cell Calcium. 2016 Aug;60(2):142-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2016.03.006. Epub 2016 Mar 19. Cell Calcium. 2016. PMID: 27041216 Review.
Cited by
-
LDL-c/HDL-c Ratio and NADPH-Oxidase-2-Derived Oxidative Stress as Main Determinants of Microvascular Endothelial Function in Morbidly Obese Subjects.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Sep 20;13(9):1139. doi: 10.3390/antiox13091139. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39334798 Free PMC article.
-
ORAI Ca2+ Channels in Cancers and Therapeutic Interventions.Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 29;14(4):417. doi: 10.3390/biom14040417. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38672434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orai1 Expression and Vascular Function in Kidney Donors Determine Graft Outcomes at Short/Mid-Term.Cells. 2025 Jul 1;14(13):1005. doi: 10.3390/cells14131005. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40643525 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benjamin E.J., Muntner P., Alonso A., Bittencourt M.S., Callaway C.W., Carson A.P., Chamberlain A.M., Chang A.R., Cheng S., Das S.R., et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139:e56–e528. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rodríguez-Mañas L., El-Assar M., Vallejo S., López-Dóriga P., Solís J., Petidier R., Montes M., Nevado J., Castro M., Gómez-Guerrero C., et al. Endothelial dysfunction in aged humans is related with oxidative stress and vascular inflammation. Aging Cell. 2009;8:226–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2009.00466.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

