TRIM67 Implicates in Regulating the Homeostasis and Synaptic Development of Mitral Cells in the Olfactory Bulb
- PMID: 37686246
- PMCID: PMC10487898
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241713439
TRIM67 Implicates in Regulating the Homeostasis and Synaptic Development of Mitral Cells in the Olfactory Bulb
Abstract
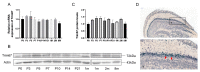
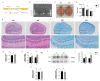
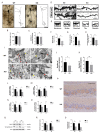
In recent years, olfactory dysfunction has attracted increasingly more attention as a hallmark symptom of neurodegenerative diseases (ND). Deeply understanding the molecular basis underlying the development of the olfactory bulb (OB) will provide important insights for ND studies and treatments. Now, with a genetic knockout mouse model, we show that TRIM67, a new member of the tripartite motif (TRIM) protein family, plays an important role in regulating the proliferation and development of mitral cells in the OB. TRIM67 is abundantly expressed in the mitral cell layer of the OB. The genetic deletion of TRIM67 in mice leads to excessive proliferation of mitral cells in the OB and defects in its synaptic development, resulting in reduced olfactory function in mice. Finally, we show that TRIM67 may achieve its effect on mitral cells by regulating the Semaphorin 7A/Plexin C1 (Sema7A/PlxnC1) signaling pathway.
Keywords: TRIM67; development; mitral cells; olfactory bulb.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

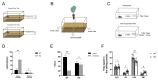
Similar articles
-
Loss of TRIM67 Attenuates the Progress of Obesity-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 5;23(13):7475. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137475. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806477 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM67 Activates p53 to Suppress Colorectal Cancer Initiation and Progression.Cancer Res. 2019 Aug 15;79(16):4086-4098. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3614. Epub 2019 Jun 25. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31239268
-
Ameliorating Effects of TRIM67 against Intestinal Inflammation and Barrier Dysfunction Induced by High Fat Diet in Obese Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 11;23(14):7650. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147650. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887011 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related impairment of olfactory bulb neurogenesis in the Ts65Dn mouse model of Down syndrome.Exp Neurol. 2014 Jan;251:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.10.018. Epub 2013 Nov 2. Exp Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24192151
-
The Olfactory System as Marker of Neurodegeneration in Aging, Neurological and Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jun 29;18(13):6976. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18136976. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34209997 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Graven S.N., Browne J.V. Sensory development in the fetus, neonate, and infant: Introduction and overview. Newborn Infant Nurs. Rev. 2008;8:169–172. doi: 10.1053/j.nainr.2008.10.007. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

