Identification and Characterization of RK22, a Novel Antimicrobial Peptide from Hirudinaria manillensis against Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 37686259
- PMCID: PMC10487658
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241713453
Identification and Characterization of RK22, a Novel Antimicrobial Peptide from Hirudinaria manillensis against Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
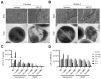
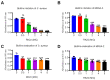
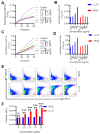
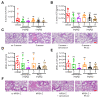
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) infections are a leading cause of morbidity and mortality, which are compounded by drug resistance. By manipulating the coagulation system, S. aureus gains a significant advantage over host defense mechanisms, with hypercoagulation induced by S. aureus potentially aggravating infectious diseases. Recently, we and other researchers identified that a higher level of LL-37, one endogenous antimicrobial peptide with a significant killing effect on S. aureus infection, resulted in thrombosis formation through the induction of platelet activation and potentiation of the coagulation factor enzymatic activity. In the current study, we identified a novel antimicrobial peptide (RK22) from the salivary gland transcriptome of Hirudinaria manillensis (H. manillensis) through bioinformatic analysis, and then synthesized it, which exhibited good antimicrobial activity against S. aureus, including a clinically resistant strain with a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 6.25 μg/mL. The RK22 peptide rapidly killed S. aureus by inhibiting biofilm formation and promoting biofilm eradication, with good plasma stability, negligible cytotoxicity, minimal hemolytic activity, and no significant promotion of the coagulation system. Notably, administration of RK22 significantly inhibited S. aureus infection and the clinically resistant strain in vivo. Thus, these findings highlight the potential of RK22 as an ideal treatment candidate against S. aureus infection.
Keywords: Hirudinaria manillensis; RK22; Staphylococcus aureus; antimicrobial peptide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Vella V., Galgani I., Polito L., Arora A.K., Creech C.B., David M.Z., Lowy F.D., Macesic N., Ridgway J.P., Uhlemann A.C., et al. Staphylococcus aureus Skin and Soft Tissue Infection Recurrence Rates in Outpatients: A Retrospective Database Study at 3 US Medical Centers. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2021;73:e1045–e1053. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1717. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022YFC2105003/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- U2002219/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- KFJ-BRP-008-003 and SAJC202103/Chinese Academy of Sciences
- 202003AD150008 and 202302AA310035/Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department
- 2022SCP007/Kunming Science and Technology Bureau
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

