BAP31 Knockout in Macrophages Affects CD4+T Cell Activation through Upregulation of MHC Class II Molecule
- PMID: 37686286
- PMCID: PMC10487781
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241713476
BAP31 Knockout in Macrophages Affects CD4+T Cell Activation through Upregulation of MHC Class II Molecule
Abstract
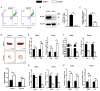
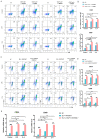
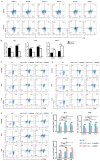
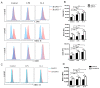
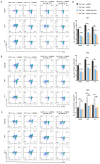
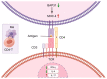
The differentiation of CD4+T cells is a crucial component of the immune response. The spleen and thymus, as immune organs, are closely associated with the differentiation and development of T cells. Previous studies have suggested that BAP31 may play a role in modulating T cell activation, but the specific impact of BAP31 on T cells through macrophages remains uncertain. In this study, we present evidence that BAP31 macrophage conditional knockout (BAP31-MCKO) mice display an enlarged spleen and thymus, accompanied by activated clustering and disrupted differentiation of CD4+T cells. In vitro co-culture studies were conducted to investigate the impact of BAP31-MCKO on the activation and differentiation of CD4+T cells. The examination of costimulatory molecule expression in BMDMs and RAW 264.7 cells, based on the endoplasmic reticulum function of BAP31, revealed an increase in the expression of antigen presenting molecules, particularly MHC-II molecule, in the absence of BAP31 in BMDMs or RAW264.7 cells. These findings suggest that BAP31 plays a role in the activation and differentiation of CD4+T cells by regulating the MHC class II molecule on macrophages. These results provide further support for the importance of BAP31 in developing interaction between macrophages and CD4+T cells.
Keywords: BAP31; CD4+T cell; MHC-II; activation; differentiation; macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

