Metabolomic Analysis of Pediatric Patients with Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury According to the Updated RUCAM
- PMID: 37686369
- PMCID: PMC10487599
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241713562
Metabolomic Analysis of Pediatric Patients with Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury According to the Updated RUCAM
Abstract
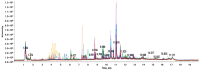
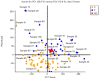
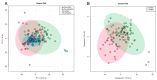
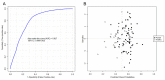
Hepatotoxicity, a common adverse drug effect, has been extensively studied in adult patients. However, it is equally important to investigate this condition in pediatric patients to develop personalized treatment strategies for children. This study aimed to identify plasma biomarkers that characterize hepatotoxicity in pediatric patients through an observational case-control study. Metabolomic analysis was conducted on 55 pediatric patients with xenobiotic liver toxicity and 88 healthy controls. The results revealed clear differences between the two groups. Several metabolites, including hydroxydecanoylcarnitine, octanoylcarnitine, lysophosphatidylcholine, glycocholic acid, and taurocholic acid, were identified as potential biomarkers (area under the curve: 0.817; 95% confidence interval: 0.696-0.913). Pathway analysis indicated involvement of primary bile acid biosynthesis and the metabolism of taurine and hypotaurine (p < 0.05). The findings from untargeted metabolomic analysis demonstrated an increase in bile acids in children with hepatotoxicity. The accumulation of cytotoxic bile acids should be further investigated to elucidate the role of these metabolites in drug-induced liver injury.
Keywords: DILI; bile acids; children; liver injury; metabolomics; updated RUCAM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Ye L., Feng Z., Huang L., Guo C., Wu X., He L., Tan W., Wang Y., Wu X., Hu B., et al. Causality Evaluation of Drug-Induced Liver Injury in Newborns and Children in the Intensive Care Unit Using the Updated Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method. Front. Pharmacol. 2021;12:790108. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.790108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

