Preliminary Comparison of Molecular Antioxidant and Inflammatory Mechanisms Determined in the Peripheral Blood Granulocytes of COVID-19 Patients
- PMID: 37686388
- PMCID: PMC10488240
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241713574
Preliminary Comparison of Molecular Antioxidant and Inflammatory Mechanisms Determined in the Peripheral Blood Granulocytes of COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
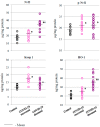
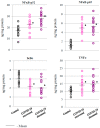
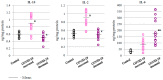
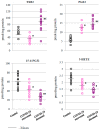
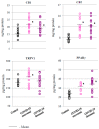
The aim of this study was to evaluate selected parameters of redox signaling and inflammation in the granulocytes of COVID-19 patients who recovered and those who died. Upon admission, the patients did not differ in terms of any relevant clinical parameter apart from the percentage of granulocytes, which was 6% higher on average in those patients who died. Granulocytes were isolated from the blood of 15 healthy people and survivors and 15 patients who died within a week, and who were selected post hoc for analysis according to their matching gender and age. They differed only in the lethal outcome, which could not be predicted upon arrival at the hospital. The proteins level (respective ELISA), antioxidant activity (spectrophotometry), and lipid mediators (UPUPLC-MS) were measured in the peripheral blood granulocytes obtained via gradient centrifugation. The levels of Nrf2, HO-1, NFκB, and IL-6 were higher in the granulocytes of COVID-19 patients who died within a week, while the activity of cytoplasmic Cu,Zn-SOD and mitochondrial Mn-SOD and IL-2/IL-10 were lower in comparison to the levels observed in survivors. Furthermore, in the granulocytes of those patients who died, an increase in pro-inflammatory eicosanoids (PGE2 and TXB2), together with elevated cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2 (associated with a decrease in the anti-inflammatory 15d-PGJ2), were found. Hence, this study suggests that by triggering transcription factors, granulocytes activate inflammatory and redox signaling, leading to the production of pro-inflammatory eicosanoids while reducing cellular antioxidant capacity through SOD, thus expressing an altered response to COVID-19, which may result in the onset of systemic oxidative stress, ARDS, and the death of the patient.
Keywords: COVID-19; G protein-coupled receptors; antioxidants; eicosanoids; granulocytes; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diversified Effects of COVID-19 as a Consequence of the Differential Metabolism of Phospholipids and Lipid Peroxidation Evaluated in the Plasma of Survivors and Deceased Patients upon Admission to the Hospital.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 5;23(19):11810. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911810. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233111 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Severe COVID-19 on Plasma Antioxidants.Molecules. 2022 Aug 21;27(16):5323. doi: 10.3390/molecules27165323. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36014561 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiological Alterations of Redox Signaling and Endocannabinoid System in Granulocytes and Plasma of Psoriatic Patients.Cells. 2018 Oct 6;7(10):159. doi: 10.3390/cells7100159. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30301214 Free PMC article.
-
Dual effects of supplemental oxygen on pulmonary infection, inflammatory lung injury, and neuromodulation in aging and COVID-19.Free Radic Biol Med. 2022 Sep;190:247-263. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.08.004. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35964839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress and gene transcription in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: antioxidant therapeutic targets.Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2002 Sep;1(3):291-315. doi: 10.2174/1568010023344607. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2002. PMID: 14561194 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of CRTH2 as a New PPARγ-Target Gene in T Cells Suggested CRTH2 Dependent Conversion of Th2 Cells as Therapeutic Concept in COVID-19 Infection.Immunotargets Ther. 2024 Nov 2;13:595-616. doi: 10.2147/ITT.S463601. eCollection 2024. Immunotargets Ther. 2024. PMID: 39507298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rizzi M., D’Onghia D., Tonello S., Minisini R., Colangelo D., Bellan M., Castello L.M., Gavelli F., Avanzi G.C., Pirisi M., et al. COVID-19 Biomarkers at the Crossroad between Patient Stratification and Targeted Therapy: The Role of Validated and Proposed Parameters. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023;24:7099. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087099. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Passariello M., Esposito S., Manna L., Rapuano Lembo R., Zollo I., Sasso E., Amato F., De Lorenzo C. Comparative Analysis of a Human Neutralizing MAb Specific for SARS-CoV-2 Spike-RBD with Cilgavimab and Tixagevimab for the Efficacy on the Omicron Variant in Neutralizing and Detection Assays. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023;24:10053. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210053. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Giamarellos-Bourboulis E.J., Netea M.G., Rovina N., Akinosoglou K., Antoniadou A., Antonakos N., Damoraki G., Gkavogianni T., Adami M.-E., Katsaounou P., et al. Complex Immune Dysregulation in COVID-19 Patients with Severe Respiratory Failure. Cell Host Microbe. 2020;27:992–1000.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.04.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

