The Dutch CAR-T Tumorboard Experience: Population-Based Real-World Data on Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma Referred for CD19-Directed CAR T-Cell Therapy in The Netherlands
- PMID: 37686611
- PMCID: PMC10486925
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15174334
The Dutch CAR-T Tumorboard Experience: Population-Based Real-World Data on Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma Referred for CD19-Directed CAR T-Cell Therapy in The Netherlands
Abstract
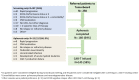
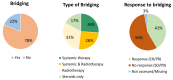
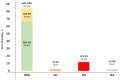
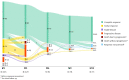
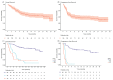
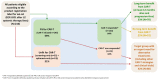
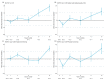
The real-world results of chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy for patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) substantially differ across countries. In the Netherlands, the CAR-T tumorboard facilitates a unique nationwide infrastructure for referral, eligibility assessment and data collection. The aim of this study was to evaluate real-world outcomes of axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) in the Dutch population, including the thus-far underreported effects on health-related quality of life (HR-QoL). All patients with R/R LBCL after ≥2 lines of systemic therapy referred for axi-cel treatment between May 2020-May 2022 were included (N = 250). Of the 160 apheresed patients, 145 patients received an axi-cel infusion. The main reason for ineligibility was rapidly progressive disease. The outcomes are better or at least comparable to other studies (best overall response rate: 84% (complete response: 66%); 12-month progression-free-survival rate and overall survival rate: 48% and 62%, respectively). The 12-month NRM was 5%, mainly caused by infections. Clinically meaningful improvement in several HR-QoL domains was observed from Month 9 onwards. Expert-directed patient selection can support effective and sustainable application of CAR-T treatment. Matched comparisons between cohorts will help to understand the differences in outcomes across countries and select best practices. Despite the favorable results, for a considerable proportion of patients with R/R LBCL there still is an unmet medical need.
Keywords: CAR T-cell therapy; LBCL; outcomes; real-world data.
Conflict of interest statement
M.J. received honoraria from Kite/Gilead and BMS/Celgene, has a consulting/advisory role for Janssen and received research funding from Novartis. A.G.H.N. discloses conflicts of interest all outside of the submitted work with: IBA, PHILIPS, MIRADA, RaySearch, Siemens, Elekta, Leonie and Genentech. M.W.M.v.d.P. received honoraria from Kite/Gilead and Takeda. M.T.K. has a consulting/advisory role for CellPoint. M.E.D.C. has a consulting/advisory role for AbbVie and Novartis and received research funding from BMS/Celgene, Gilead and GenMAb. P.J.L. received honoraria for advisory boards from Genmab, AbbVie, Roche, Regeneron and Incyte, has a consulting role for Y-mAbs Therapeutics, is in the speakers’ bureau for Lilly and AbbVie, and has received travel support from Celgene and research funding from Takeda and Servier. M.C.M. has a consulting/advisory role for Janssen Cilag, CDR life, GSK and the speakers’ bureau for Doen, Janssen Cilag, BMS, WebMD global. T.v.M. has served on the advisory boards of Kite/Gilead, Celgene/BMS, Jansen and Lilly and received research funding from Kite/Gilead, Celgene/BMS, Genentech and Siemens. M.J.K. received honoraria from and performed in a consulting/advisory role for BMS/Celgene, Kite, a Gilead Company, Miltenyi Biotec, Novartis and Roche, as well as receiving research funding from Kite, a Gilead Company, Roche, Takeda, and Celgene and travel support from Kite, a Gilead Company, Miltenyi Biotec, Novartis, and Roche (all to institutions). A.M.S., E.R.A.P., P.G.N.J.M., S.v.D., J.A.v.D., J.W.d.B., M.K., J.S.P.V., A.S.-S., I.S.N., J.K.D. and Y.I.M.S. declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Crump M., Neelapu S.S., Farooq U., Van Den Neste E., Kuruvilla J., Westin J., Link B.K., Hay A., Cerhan J.R., Zhu L., et al. Outcomes in refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Results from the international SCHOLAR-1 study. Blood. 2017;130:1800–1808. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-03-769620. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Neelapu S.S., Locke F.L., Bartlett N.L., Lekakis L.J., Miklos D.B., Jacobson C.A., Braunschweig I., Oluwole O.O., Siddiqi T., Lin Y., et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017;377:2531–2544. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1707447. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abramson J.S., Palomba M.L., Gordon L.I., Lunning M.A., Wang M., Arnason J., Mehta A., Purev E., Maloney D.G., Andreadis C., et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): A multicentre seamless design study. Lancet. 2020;396:839–852. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31366-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Locke F.L., Ghobadi A., Jacobson C.A., Miklos D.B., Lekakis L.J., Oluwole O.O., Lin Y., Braunschweig I., Hill B.T., Timmerman J.M., et al. Long-term safety and activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma (ZUMA-1): A single-arm, multicentre, phase 1–2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:31–42. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30864-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 875171/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement No. 875171, QUALITOP
- 116026/Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 Joint Undertaking (grant agreement No. 116026), T2EVOLVE. This Joint Undertaking receives support from the European Union's Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation program and European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

