Exploring the Network between Adipocytokines and Inflammatory Response in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 37686837
- PMCID: PMC10490077
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15173806
Exploring the Network between Adipocytokines and Inflammatory Response in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Scoping Review
Abstract
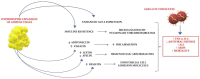
Adipose tissue is actually regarded as an endocrine organ, rather than as an organ that merely stores energy. During the COVID-19 pandemic, obesity has undoubtedly emerged as one of the most important risk factors for disease severity and poor outcomes related to SARS-CoV-2 infection. The aberrant production of cytokine-like hormones, called adipokines, may contribute to alterations in metabolism, dysfunction in vascular endothelium and the creation of a state of general chronic inflammation. Moreover, chronic, low-grade inflammation linked to obesity predisposes the host to immunosuppression and excessive cytokine activation. In this respect, understanding the mechanisms that link obesity with the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection could represent a real game changer in the development of new therapeutic strategies. Our review therefore examines the pathogenic mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2, the implications with visceral adipose tissue and the influences of the adipose tissue and its adipokines on the clinical behavior of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; adipocytokines; adiponectin; leptin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Scialo F., Vitale M., Daniele A., Nigro E., Perrotta F., Gelzo M., Iadevaia C., Cerqua F.S., Costigliola A., Allocca V., et al. SARS-CoV-2: One Year in the Pandemic. What Have We Learned, the New Vaccine Era and the Threat of SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Biomedicines. 2021;9:611. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9060611. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

