Molecular Docking Assessment of Cathinones as 5-HT2AR Ligands: Developing of Predictive Structure-Based Bioactive Conformations and Three-Dimensional Structure-Activity Relationships Models for Future Recognition of Abuse Drugs
- PMID: 37687065
- PMCID: PMC10488745
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28176236
Molecular Docking Assessment of Cathinones as 5-HT2AR Ligands: Developing of Predictive Structure-Based Bioactive Conformations and Three-Dimensional Structure-Activity Relationships Models for Future Recognition of Abuse Drugs
Abstract
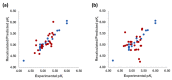
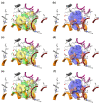
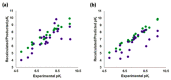
Commercially available cathinones are drugs of long-term abuse drugs whose pharmacology is fairly well understood. While their psychedelic effects are associated with 5-HT2AR, the enclosed study summarizes efforts to shed light on the pharmacodynamic profiles, not yet known at the receptor level, using molecular docking and three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship (3-D QSAR) studies. The bioactive conformations of cathinones were modeled by AutoDock Vina and were used to build structure-based (SB) 3-D QSAR models using the Open3DQSAR engine. Graphical inspection of the results led to the depiction of a 3-D structure analysis-activity relationship (SAR) scheme that could be used as a guideline for molecular determinants by which any untested cathinone molecule can be predicted as a potential 5-HT2AR binder prior to experimental evaluation. The obtained models, which showed a good agreement with the chemical properties of co-crystallized 5-HT2AR ligands, proved to be valuable for future virtual screening campaigns to recognize unused cathinones and similar compounds, such as 5-HT2AR ligands, minimizing both time and financial resources for the characterization of their psychedelic effects.
Keywords: 3-D QSAR; 5-HT2AR; cathinones; molecular docking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Matsumoto T., Kobayashi T., Ishida K., Taguchi K., Kamata K. Enhancement of Mesenteric Artery Contraction to 5-HT Depends on Rho Kinase and Src Kinase Pathways in the Ob/Ob Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010;160:1092–1104. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00753.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

