A Comprehensive Review on Bioactive Compounds Found in Caesalpinia sappan
- PMID: 37687076
- PMCID: PMC10488625
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28176247
A Comprehensive Review on Bioactive Compounds Found in Caesalpinia sappan
Abstract
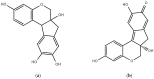
Sappan wood (Caesalpinia sappan) is a tropical hardwood tree found in Southeast Asia. Sappan wood contains a water-soluble compound, which imparts a red color named brazilin. Sappan wood is utilized to produce dye for fabric and coloring agents for food and beverages, such as wine and meat. As a valuable medicinal plant, the tree is also known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties. It has been observed that sappan wood contains various bioactive compounds, including brazilin, brazilein, sappan chalcone, and protosappanin A. It has also been discovered that these substances have various health advantages; they lower inflammation, enhance blood circulation, and are anti-oxidative in nature. Sappan wood has been used as a medicine to address a range of illnesses, such as gastrointestinal problems, respiratory infections, and skin conditions. Studies have also suggested that sappan wood may have anticarcinogenic potential as it possesses cytotoxic activity against cancer cells. Based on this, the present review emphasized the different medicinal properties, the role of phytochemicals, their health benefits, and several food and nonfood applications of sappan wood. Overall, sappan wood has demonstrated promising medicinal properties and is an important resource in traditional medicine. The present review has explored the potential role of sappan wood as an essential source of bioactive compounds for drug development.
Keywords: Brazilwood; Indian Redwood; Suou; chemical constituents; coloring agent; heartwood; sappan wood.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Badami S., Moorkoth S. Caesalpinia sappan–A medicinal and dye yielding plant. Nat. Prod. Radiance. 2004;3
-
- Thanayutsiri T., Patrojanasophon P., Opanasopit P., Ngawhirunpat T., Laiwattanapaisal W., Rojanarata T. Rapid and efficient microwave-assisted extraction of Caesalpinia sappan Linn. heartwood and subsequent synthesis of gold nanoparticles. Green. Process. Synth. 2023;12:20228109. doi: 10.1515/gps-2022-8109. - DOI
-
- Mekala K., Radha R. A Review on Sappan Wood-A Therapeutic Dye Yielding Tree. Res. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2015;7:227. doi: 10.5958/0975-4385.2015.00035.7. - DOI
-
- Mathew G., Skaria B.P., Mathew S., Joy P.P. Caesalpinia Sappan-an Economic Medicinal Tree for the Tropics; Proceedings of the National Symposium on Medicinal and Aromatic Plants for the Economic Benefit of Rural People (MAPER); Thiruvananthapuram, India. 16–18 February 2007; pp. 1–7.
-
- Rosniawaty S., Anjarsari I.R.D., Sudirja R., Mubarok S., Fatmawati D. Effect of growth regulators and organic matter on the growth of Sappan wood seedlings (Caesalpinia sappan L.) Res. Crops. 2023;24:198–209. doi: 10.31830/2348-7542.2023.ROC-896. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

