Comparison of Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activities in Differentially Pigmented Cerasus humilis Fruits
- PMID: 37687101
- PMCID: PMC10488777
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28176272
Comparison of Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activities in Differentially Pigmented Cerasus humilis Fruits
Abstract
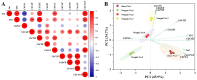
Chinese dwarf cherry (Cerasus humilis) is a wild fruit tree and medicinal plant endemic to China. Its fruits are rich in various bioactive compounds, such as flavonoids and carotenoids, which contribute greatly to their high antioxidant capacity. In this study, the contents of bioactive substances (chlorophyll, carotenoids, ascorbic acid, anthocyanin, total flavonoids, and total phenols), antioxidant capacities, 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and 2,2'-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonicacid) (ABTS+) scavenging ability, and ferric-reducing antioxidant power (FRAP)) in differentially pigmented C. humilis fruits of four varieties were determined and compared. The results revealed that anthocyanin, total flavonoids and total phenols were the three main components responsible for the antioxidant activity of C. humilis fruits. 'Jinou No.1' fruits with dark red peel and red flesh had the highest contents of anthocyanin, total flavonoids, and total phenols, as well as the highest antioxidant capacities; 'Nongda No.5' fruits with yellow-green peel and yellow flesh had the highest contents of carotenoids and chlorophyll, while 'Nongda No.6' fruit had the highest ascorbic acid content. To further reveal the molecular mechanism underlying differences in the accumulation of carotenoids and flavonoids among differentially pigmented C. humilis fruits, the expression patterns of structural genes involved in the biosynthesis of the two compounds were investigated. Correlation analysis results revealed that the content of carotenoids in C. humilis fruits was very significantly positively correlated with the expression of the ChCHYB, ChZEP, ChVDE, ChNSY, ChCCD1, ChCCD4, ChNCED1, and ChNCED5 genes (p < 0.01) and significantly negatively correlated with the expression of ChZDS (p < 0.05). The anthocyanin content was very significantly positively correlated with ChCHS, ChFLS, and ChUFGT expression (p < 0.01). The total flavonoid content was very significantly positively correlated with the expression of ChCHS, ChUFGT, and ChC4H (p < 0.01) and significantly positively correlated with ChFLS expression (p < 0.05). This study can provide a basis for understanding the differences in the accumulation of bioactive substances, and is helpful for clarifying the mechanisms underlying the accumulation of various carotenoids and flavonoids among differentially pigmented C. humilis fruits.
Keywords: Cerasus humilis; antioxidant capacity; bioactive substances; carotenoids; flavonoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Changes of bioactive components and antioxidant potential during fruit development of Prunus humilis Bunge.PLoS One. 2021 May 19;16(5):e0251300. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0251300. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34010329 Free PMC article.
-
ChBBX6 and ChBBX18 are positive regulators of anthocyanins biosynthesis and carotenoids degradation in Cerasus humilis.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Dec;282(Pt 4):137195. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.137195. Epub 2024 Nov 1. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39489264
-
Comparative and Correlational Evaluation of the Phytochemical Constituents and Antioxidant Activity of Musa sinensis L. and Musa paradisiaca L. Fruit Compartments (Musaceae).ScientificWorldJournal. 2020 Aug 6;2020:4503824. doi: 10.1155/2020/4503824. eCollection 2020. ScientificWorldJournal. 2020. PMID: 32831803 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of High-Pressure Processing on Antioxidant Activity during Storage of Fruits and Fruit Products: A Review.Molecules. 2021 Aug 30;26(17):5265. doi: 10.3390/molecules26175265. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34500700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fruit ripening: dynamics and integrated analysis of carotenoids and anthocyanins.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Jan 11;22(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03411-w. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35016620 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Piriformospora indica culture filtrate application adds brilliance to the promoting effects of facility warming on winter jujube fruit ripening.Food Chem X. 2024 Nov 9;24:101986. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101986. eCollection 2024 Dec 30. Food Chem X. 2024. PMID: 39618556 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific responses of Taxus mairei to UV-B radiation involved altering the interactions between the microbiota assembly and host secondary metabolism.Microbiome. 2024 Sep 7;12(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s40168-024-01882-1. Microbiome. 2024. PMID: 39244575 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Reveal Key Genes and Metabolic Pathway in Flower and Fruit Color Formation of Cerasus humilis (Bge.) Sok.Plants (Basel). 2025 Apr 2;14(7):1103. doi: 10.3390/plants14071103. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40219170 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome identification of HSF family genes in Cerasus humilis and expression analysis under high-temperature stress.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Apr 28;16:1553187. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1553187. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40357146 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Characterization of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis-Related Dihydroflavonol 4-reductase (DFR) Genes in Blueberries (Vaccinium corymbosum).Plants (Basel). 2025 May 13;14(10):1449. doi: 10.3390/plants14101449. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40431014 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neupane P., Lamichhane J. Estimation of total phenolic content, total flavonoid content and antioxidant capacities of five medicinal plants from Nepal. Vegetos. 2020;33:360–366. doi: 10.1007/s42535-020-00116-7. - DOI
-
- Popova M.P., Bankova V.S., Bogdanov S., Tsvetkova I., Naydenski C., Marcazzan G.L., Sabatini A.-G. Chemical characteristics of poplar type propolis of different geographic origin. Apidologie. 2007;38:306–311. doi: 10.1051/apido:2007013. - DOI
-
- Marinova D., Ribarova F. HPLC determination of carotenoids in Bulgarian berries. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2007;20:370–374. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2006.09.007. - DOI
-
- Khalid W., Iqra, Afzal F., Rahim M.A., Abdul Rehman A., Faiz ul Rasul H., Arshad M.S., Ambreen S., Zubair M., Safdar S., et al. Industrial applications of kale (Brassica oleracea var. sabellica) as a functional ingredient: A review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2023;26:489–501. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2023.2168011. - DOI
-
- Bajalan I., Mohammadi M., Alaei M., Pirbalouti A.G. Total phenolic and flavonoid contents and antioxidant activity of extracts from different populations of lavandin. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016;87:255–260. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.04.059. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

