Phenolic Profiles, Antihyperglycemic, Anti-Diabetic, and Antioxidant Properties of Egyptian Sonchus oleraceus Leaves Extract: An In Vivo Study
- PMID: 37687218
- PMCID: PMC10489745
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28176389
Phenolic Profiles, Antihyperglycemic, Anti-Diabetic, and Antioxidant Properties of Egyptian Sonchus oleraceus Leaves Extract: An In Vivo Study
Abstract
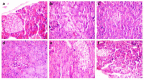
This study aimed to investigate the phenolic and antioxidant properties of Egyptian Sonchus oleraceus leaves extract (SOE) while comparing the antihyperglycemic efficacy of SOE with that of conventional medicines (glibenclamide) in vivo as a substitution for insulin-deficient patients. Total phenolic (TPC) and flavonoid contents (TFC) in SOE contributed around 127.66 ± 0.56 mg GAE/gm as gallic acid equivalent (GAE) and 74.80 ± 0.55 mg QE/gm as quercetin equivalent (QE). SOE also showed significant DPPH scavenging activity at 43.46%. The presence of five phenolic and six flavonoid compounds in SOE was discovered by HPLC analysis. For the in vivo assay, 42 rats were distributed into six groups (7 Wister albino rats each). The standard control group was fed a basal diet. While the 35 rats were induced with a single dose of 100 mg kg-1 body weight (b.w.) alloxan, then treated orally with glibenclamide (GLI) at 10 mg kg-1, 100, 200, and 300 mg kg-1 SOE (positive control group) for 56 days of routine gastric oral gavages and compared to the effects of GLI, the treatment of SOE 200 and 300 mg kg-1 in diabetic rats for two months dramatically decreased blood glucose, total lipid, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDLC) while boosting high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDLC) levels and improving liver and kidney functions. The histological assay revealed that the SOE 300 mg kg-1 treatment significantly improved the pancreas tissues, implying the potential application of Egyptian SOE as a diabetes treatment.
Keywords: DPPH; Sonchus oleraceus; and flavonoid; hyperglycemic; total phenolic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phenolic profiles, antihyperglycemic, antihyperlipidemic, and antioxidant properties of pomegranate (Punica granatum) peel extract.J Food Biochem. 2019 Apr;43(4):e12803. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.12803. Epub 2019 Feb 11. J Food Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31353600
-
Antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant properties of ethanol extract of Grewia asiatica Linn. bark in alloxan-induced diabetic rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Aug 18;16:295. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1276-9. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27538464 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of acute oral toxicity, anti-diabetic and antioxidant effects of Aloe vera flowers extract.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Jun 12;309:116310. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116310. Epub 2023 Feb 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36863642
-
Acacia jacquemontii ethyl acetate extract reduces hyperglycemia and pro-inflammatory markers while increasing endogenous antioxidant potential in alloxan-induced diabetic rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Jul;29(35):52605-52617. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-19493-4. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35262888
-
Phenolic content and anti-hyperglycemic activity of pecan cultivars from Egypt.Pharm Biol. 2016;54(5):788-98. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2015.1080732. Epub 2015 Oct 8. Pharm Biol. 2016. PMID: 26450069
Cited by
-
A comprehensive review on anti-inflammatory plants: a mechanistic insight through preclinical and clinical studies.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 May;33(5):2447-2476. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01764-4. Epub 2025 Jun 4. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40465037 Review.
-
Overview of Ethnobotanical-Pharmacological Studies Carried Out on Medicinal Plants from the Serra da Estrela Natural Park: Focus on Their Antidiabetic Potential.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Mar 25;16(4):454. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16040454. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38675115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking the therapeutic potential of Catharanthus roseus leaves via in-vitro, in-vivo, and in-silico study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 17;15(1):25909. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96643-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40676081 Free PMC article.
-
Cocoa and Carob Supplementation, Alone or in Combination with Metformin, Protects against Hepatorenal Injury in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 13;16(18):3087. doi: 10.3390/nu16183087. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39339687 Free PMC article.
-
Yellow mealworm frass: A promising organic fertilizer for common sowthistle (Sonchus oleraceus L.) and bristly oxtongue (Helminthotheca echioides (L.) Holub) cultivation.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 2;10(15):e35508. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35508. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saleem T., Mumtaz U., Bashir M.U., Qureshi H.J., Saleem A. Comparison of hypoglycemic effects of Azadirachta indica seeds and leaves on alloxan induced diabetes in male albino rats. Pak. J. Med. Health Sci. 2018;12:753–756.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

